Steam tracing is a type of heat tracing of process lines - using steam.
Heat tracing
Heat tracing is a small bore pipe system that is laid along process piping and equipment inside the insulation, on one or both sides - inner and outer sides - of the process pipe. Heat tracing is used for heating up a process piping system using utilities such as steam, electricity etc. In engineering, the requirement for heating of piping and instruments, using heat tracing is normally indicated on the Piping and Instrument Diagram (P&IDs) or on the line lists.
Steam Tracing
Steam tracing is heat tracing performed by circulating steam around process pipes to heat them.
Steam tracing is normally installed on:
- Stagnant piping sections such as branch connections from parallel heat exchangers or pumps, bypasses around equipment. In such piping sections, condensation or solidification could occur. Steam tracing is used to avoid this.
- Equipment or piping that needs to be prevented from winterization due to low ambient temperature conditions, utilize steam tracing.
- Suction piping of a gas compressor from the outlet of the upstream KO drum can be equipped with steam tracing to ensure no condensation occurs which could damage the compressor.
- Inlet piping of relief valves has steam tracing to ensure the piping and valve interior is kept free of any solidified material or crystallized hydrates.
Purpose of steam tracing
- Keep the fluid inside to prevent solidifying due to wax separation, crystallization and water freezing.
- Maintain the fluidity of highly viscous products, e.g. no flow situations, shutdown, isolated lines, etc.
- To avoid fluid component separation due to low temperature.
- To prevent freezing of water-containing process fluid.
- To prevent corrosive compounds forming if condensation occurs.
- To prevent condensation of gaseous process fluids.
- To prevent cold brittleness of piping material.
- To prevent hydrate formation in pipelines due to low temperature.
Steam tracing system
A steam tracing is a heat tracing which use the steam as heating medium. The heating medium of steam tracing can be saturated Low Pressure (LP) Steam or Medium Pressure (MP) Steam or High Pressure (HP) Steam. The condensing temperature can be about 150-180 0C (for LP steam) or 200-270 0C (for MP steam) and 350-400 0C (HP steam).
A steam tracing system could be:
- A closed system, in which all condensate discharge from steam traps are collected for re-use or recovery.
- An open system, when approaches are not available or rare cases in which the condensate are discharged into a drain or atmospheric.
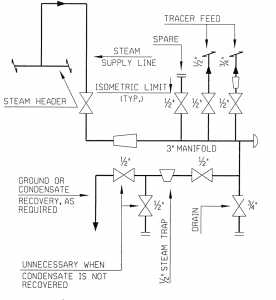
A typical piping system of steam tracing consists of:
- Traced lines: the process pipeline carrying process fluid that require steam tracing.
- Steam supply line that connects the steam supply header with the steam tracing manifold or condensate recovery line that connects the condensate header with the condensate recovery manifold.
- Steam or condensate manifold.
- Tracer line: the pipe carrying steam along the traced line.
- Steam traps: for removal of the condensate in used steam, steam traps are installed at regular intervals. It should be located at the lowest point of the tracer.
A typical steam tracing manifold installed lower than header is given as below: