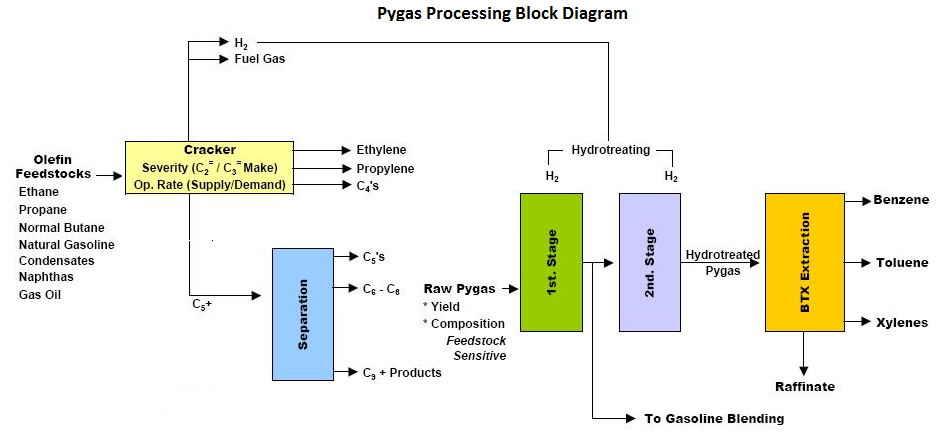
Pygas is a naphtha-range product with high aromatics content used either for gasoline blending or as a feedstock for a BTX extraction unit. Pyrolysis gasoline is produced in an ethylene plant that processes naphtha, butane or gasoil.
Pyrolosis gasoline or pygas (C5+ cut) is a liquid by-product derived from steam cracking of various hydrocarbon feedstocks in olefin plants.
This C5+ cut, if left in its raw form, has little commercial value owing to its high reactivity and low stability. However, the stream contains many high-value components, such as isoprene, benzene, toluene and xylenes.
Benzene is a key component in pygas. On a capacity basis, pygas extraction accounts for approximately 36% of global benzene.
Extracting these components can be highly economical and typically requires hydrotreating in a pygas hydrogenation unit (PHU). The stream can be treated in various ways, depending on the required product slate.
Pygas Hydrotreating
Raw pygas is first fed to the first stage hydrotreating section. To produce BTX, this C6+ stream is sent to a fractionation section to obtain a C6-C8 heart cut, which will be further hydrotreated to saturate mono-olefins in the second stage hydrotreating section.
The hydrotreating unit consists of three sections:
- First stage Hydrotreating section to saturate mainly di-olefins to olefins.
- Second stage Hydrotreating section to saturate the olefins and de-sulfurize the pygas.
- Fractionation section to stabilize the hydrotreated streams and to recover the C6-C8 heart cut for further processing for aromatics extraction and the C9+ cut.