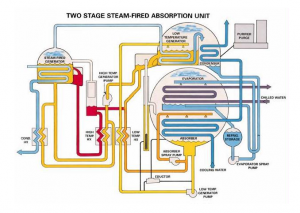
 Absorption Refrigeration Systems or Absorption Chillers - An absorption chiller produces chilled water by using the residual heat in a process plant. Pure water is usually used as refrigerant, whereas lithium bromide (LiBr) solution is used as absorbent. Usual steps in an absorption based refrigeration cycle are - evaporation of refrigerant, absorption of refrigerant vapors by LiBr, regeneration of LiBr solution by using residual waste heat, condensation of vapors etc.
Absorption Refrigeration Systems or Absorption Chillers - An absorption chiller produces chilled water by using the residual heat in a process plant. Pure water is usually used as refrigerant, whereas lithium bromide (LiBr) solution is used as absorbent. Usual steps in an absorption based refrigeration cycle are - evaporation of refrigerant, absorption of refrigerant vapors by LiBr, regeneration of LiBr solution by using residual waste heat, condensation of vapors etc.
Basics requirements of refrigerants - A refrigerant is a compound used in the refrigeration process that goes under a phase change from a gas to liquid and then back. Selection of the refrigerant to be used is most of the times project-specific and demands careful consideration. Multiple factors such as toxicity, flammability, explosivity, Ozone Depletion Potential, dew point pressure, corrosivity etc. of the refrigerant compound need to be considered when selecting a refrigerant for a specific refrigeration process.
Types of Refrigerants - Most commonly used types of refrigerants are - halocarbons or freons, azeotropic refrigerants, zeotropic refrigerants, inorganic refrigerants like carbon dioxide, ammonia, water, air etc. and hydrocarbon refrigerants.
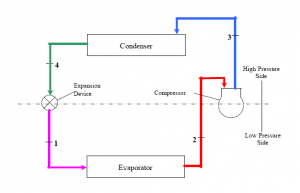 Vapor Compression Refrigeration (VCR) Cycle - A majority of big refrigeration systems in use nowadays use the Vapor Compression Refrigeration (VCR) cycle. VCR uses mechanical energy (through a compressor) as the driving force for refrigeration. A typical vapor compression refrigeration cycle goes through following steps - evaporation of liquid refrigerant, compression of the refrigerant vapors, condensation of pressurized refrigerant vapors and finally expansion of the condensed refrigerant through an expansion valve.
Vapor Compression Refrigeration (VCR) Cycle - A majority of big refrigeration systems in use nowadays use the Vapor Compression Refrigeration (VCR) cycle. VCR uses mechanical energy (through a compressor) as the driving force for refrigeration. A typical vapor compression refrigeration cycle goes through following steps - evaporation of liquid refrigerant, compression of the refrigerant vapors, condensation of pressurized refrigerant vapors and finally expansion of the condensed refrigerant through an expansion valve.
Add Comment