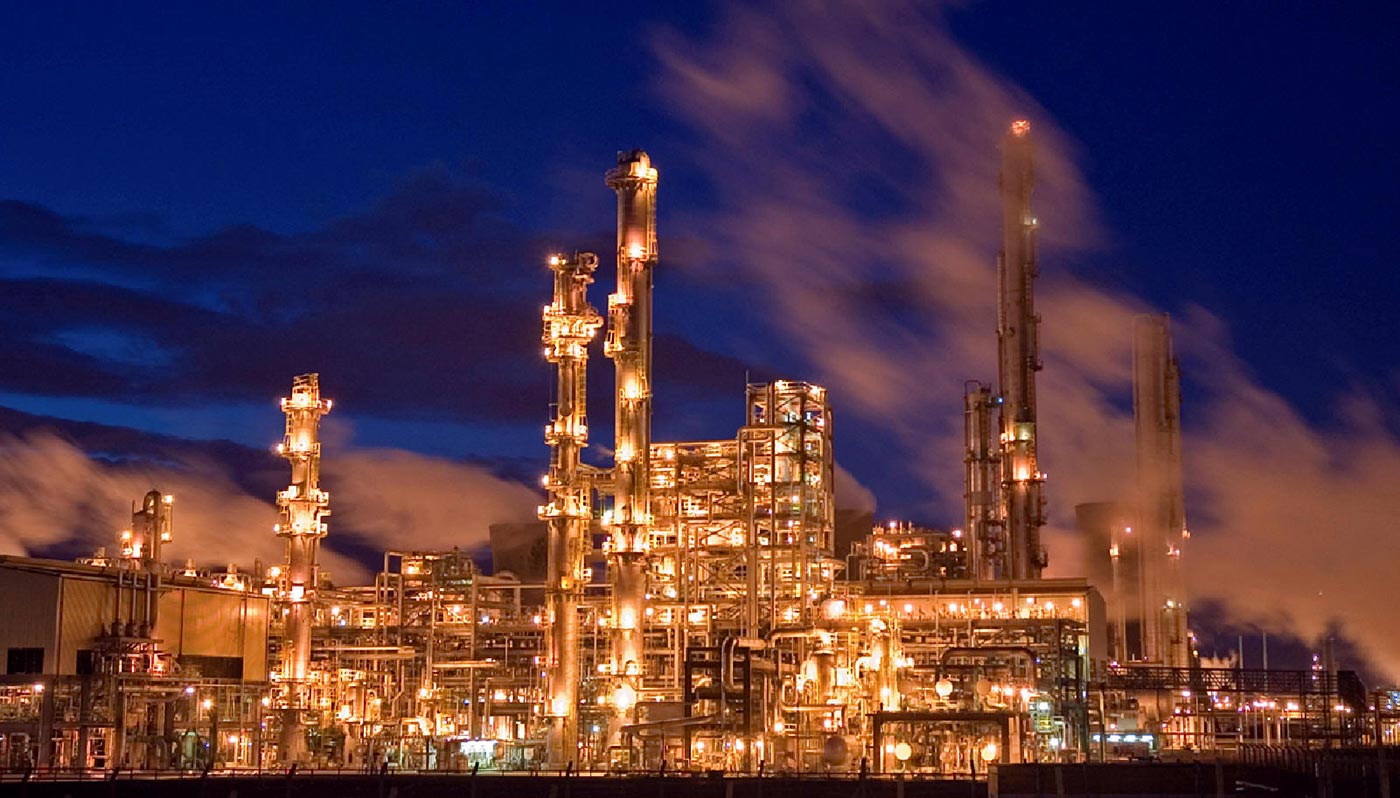
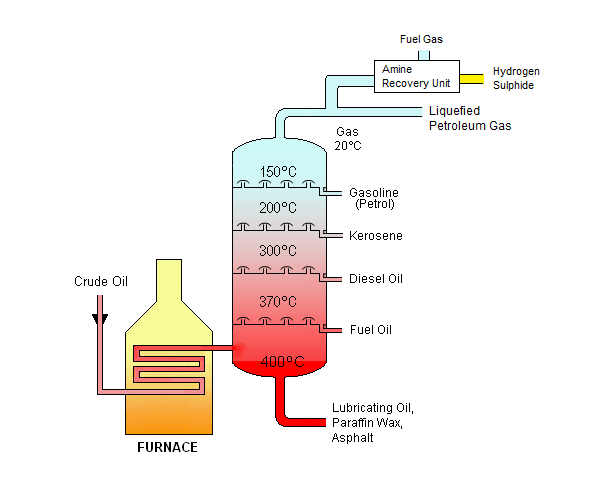
For a single component liquid without any impurities, the boiling occurs at constant temperature for a given pressure value. This temperature is known as boiling point of that liquid and it depends only on the pressure. A pure liquid component, can be completely vaporized at a single temperature and pressure point.
But for a multicomponent liquid mixture, there is no single boiling point to vaporize the complete mixture. The boiling for such mixtures occurs over a range of temperature which depends on the components involved, pressure of the system and also the affinity they have for each other. For such mixtures, the initial boiling point at a given pressure is defined as the temperature value when the first bubble of vapor is formed from the liquid mixture. This initial boiling point for a given system is a function of pressure and composition of the mixture.
For close boiling liquids (the boiling points of pure components are close to each other) significant amount of all the components may be present at the first vapor bubble formed at initial boiling point.
For mixture where boiling points of pure components are quite different from each other, lighter component (one with lower boiling point) can be easily boiled off without having significant amounts of heavy component (with higher boiling point) in the vapor phase. These mixtures are easy to separate using batch distillation.