This tutorial will focus on pump NPSH calculation, given the details of inlet tank, pump elevation profile and suction piping. NPSHr (required) is normally specified by the pump manufacturer. Hence, NPSH calculation usually refers to the calculation of available NPSH (NPSHa). Calculation of available NPSH or NPSHa is important for deciding the line sizes on suction side of a centrifugal pump. Selecting a large enough line size is crucial for avoiding cavitation in the pump.
Table of content:
NPSH formula
NPSH calculation
NPSH formula
Before solving the sample problem, the equation used to calculate NPSH must be understood.
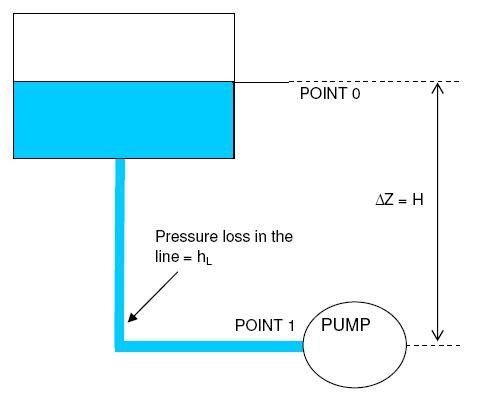
where, hL is the head loss between 0 and 1
p0 is the pressure at the water surface
pV is the vapour pressure (saturation pressure) for the fluid at the temperature T1 at 1
Δz is the difference in height z1 − z0 (shown as H on the diagram) from the water surface to the location 1
ρ is the fluid density
g is gravitational acceleration
NPSH calculation
Problem statement
Calculate the Net Positive Suction Head for a pump handling 100,000 kg/hr flow of water coming from an atmospheric storage tank. The water temperature can be taken as 250C The line size of pump suction line is 6" and the suction line is 20m long. The pump suction nozzle is 0.4 m above ground level. The tank is elevated on a 1 m high platform. The minimum liquid level in the tank is 300 mm.
Solution
This sample problem is solved in following 4 basic steps.
Step1
Important physical properties of water are first determined. Since the water is stored in an atmospheric tank at ambient conditions,
Water temperature = 250C
Water pressure = atmospheric pressure = 1.031 bar = 1 bar (approximately).
Liquid density: We need to first determine density of water at 250C. The equation for density is ρ=m/v. If you know density ρr at some temperature Tr, there is a following formula for density: ρ=ρr[1+b(T−Tr)], where ρ is the density at temperature T and b is called coefficient of cubical expansion, evaluated at reference temperature and density (ρr and Tr).
We can calculate easily it using EnggCyclopedia’s Liquid Density Calculator, water density at 250C =994.72 kg/m3
Liquid viscosity: We require value of viscosity of water at particular temperature for pump sizing calculation. We can calculate it using EnggCyclopedia’s Liquid Viscosity Calculator, water viscosity at 250C =0.90 cP
Liquid vapor pressure: Using EnggCyclopedia’s Vapor Pressure Calculator, water vapor pressure at 250C =0.032 bara
Step2
Next step to solve this sample problem is to calculate the frictional pressure loss in the suction line. This NPSH calculation can be performed using EnggCyclopedia’s pipe pressure drop calculator. As per line sizing calculator, the frictional pressure loss in the suction line is 1.3 bar/km.
Thus for a pipe length of 20m, suction line pressure loss = 1.3 X 0.02 = 0.026 bar
This pressure loss can be converted to frictional head loss,
head loss = pressure loss / ρg = 0.026x105/(994.72x9.81) = 0.27 m
In this sample problem, fittings in the suction line have not been considered.
In case there are some fittings present in the pump suction line such as valves, elbows, reducer etc., EnggCyclopedia's K-factor calculator can be used to determine the frictional pressure loss caused by these fittings.
Step3
Next step to solve the sample problem is to determine elevation difference (Δz) between pump suction and the liquid level in the storage tank. Note that for NPSH calculation always the lowest liquid level in the suction vessel or tank is considered for conservative estimate.
In the present sample problem,
Δz = elevation of tank + minimum liquid level - pump suction nozzle level
= 1 + 0.3 - 0.4 = 0.9 m
Step4
In the final of NPSH calculation, the above formula derived from NPSH definition is used.
Here, p0 = 1 bar ,
pv = 0.032 bara (water vapor pressure)
ρ = 994.72 kg/m3 (water density)
g = 9.81 m/s2 (gravitational acceleration)
Δz = 0.9 m
hL = 0.27 m
Using the NPSH equation from above,
NPSH = ((1-0.032)/(994.72x9.81))+ 0.9 - 0.27 = 10.56 m
Note that EnggCyclopedia's pump sizing calculator uses the same equation and method for NPSH calculation. It can be used to quickly determine the NPSH, instead of manually calculating it in 4 steps.
Related tutorials & calculators for NPSH calculation
- Net positive suction head - NPSH definition
- Tutorial - NPSHa calculation (for available NPSH)
- Difference between NPSHr (required) and NPSHa (available)
- Pump sizing calculator - for quick NPSHa calculation