Pumps are a critical component of many industrial processes. Their proper functioning is essential for the efficient and safe operation of many industries. However, pumps can experience issues that can reduce their performance, reliability, and safety. To ensure the proper functioning of pumps, it is crucial to test them regularly. In this post, we will discuss in methods for the testing of pumps, their importance, and how they help ensure efficient and safe pump operation.
Table of content:
Leak testing
Flow rate test
Cavitation test
Vibration test
Pump noise
Pump performance test
NPSH test
Endurance testing
Hydrostatic test
Leak testing
A pump leak occurs when fluid leaks out of a pump through its seals, which are designed to prevent the fluid from escaping. Pump leaks can have significant impacts on the pump's operation and the system it is a part of. Therefore, it is essential to detect and repair leaks promptly to prevent these issues from occurring.
Regular maintenance and testing of pump seals can help prevent leaks from occurring and ensure the smooth operation of the pump and its associated system. Different testing methods can be used to identify pump leaks and ensure the safe and efficient operation of the pump system. Here are some common methods for detecting pump leaks.


Flow rate test
Flow rate test is a fundamental technique used in pump testing to assess the performance and efficiency of a pump. The flow rate of a pump refers to the volume or mass of fluid that is moved by the pump per unit of time. It is an important parameter that affects the overall performance of the pump and its ability to meet the flow requirements of the system it is serving. This test is done in a variety of applications, such as selecting and sizing new pumps, assessing the performance of existing pumps, troubleshooting pump & system problems, and optimizing pump operation and system efficiency.
Cavitation test
Pump cavitation is a phenomenon of the formation and subsequent collapse or implosion of vapor bubbles in a pump. This can cause damage to the pump impeller and reduce the pump's efficiency, as well as create noise and vibration. To prevent cavitation from occurring, it is important to ensure that the pump is not operating beyond its design limits. A cavitation test can be performed to determine the operational envelope under which cavitation can be prevented, taking into account the characteristics of the input fluid.
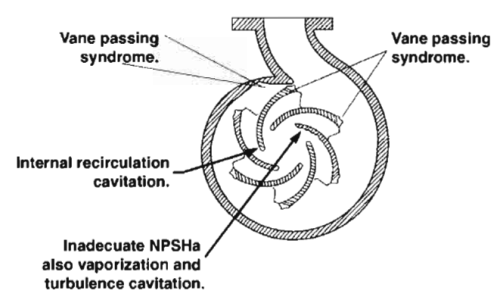
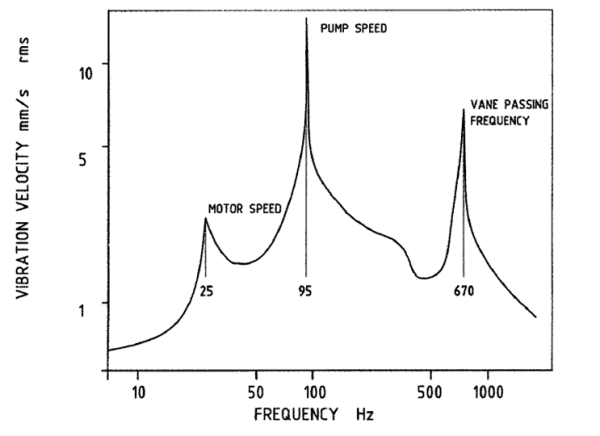
Vibration test
Vibration in pumps is a common issue in pumps and can lead to various problems that can affect the performance, reliability, and safety of the equipment. When pumps vibrate excessively, it can lead to reduced efficiency, increased wear and tear, and premature failure of pump components.
Therefore, it is important to address pump vibration promptly and effectively. By monitoring and diagnosing the cause of pump vibration, maintenance personnel can take corrective actions. This will help ensure reliable and efficient pump operation, minimize downtime, and improve safety in the workplace.
Pump noise
Pumps are mechanical devices that are used to move fluids or gases. They often involve rotating machinery, such as impellers or rotors, which can create significant amounts of noise during operation. This pump noise can be unpleasant or even harmful to those who are exposed to it for extended periods of time. Check the post to study about the noise level generated by pumps and compressors and how manufacturers test and assess the excessive noise in pumps.

Pump performance test
The purpose of pump performance test is to ensure that the actual performance of a pump is typical to that set by supplier. Typical steps to be followed to conduct a pump performance test are discusses in the post.
NPSH test
NPSH (Net Positive Suction Head) testing is an important method used during testing of pumps. NPSH refers to the amount of pressure required at the pump suction to prevent cavitation, which is the formation of bubbles or voids in the pump caused by low pressure. Cavitation can damage the impeller, reduce performance, and lead to costly breakdowns.
NPSH testing involves measuring the NPSH required by the pump to operate correctly. The test involves connecting a pressure gauge to the pump suction, measuring the pressure at the suction, and comparing it to the NPSH required by the pump. The NPSH required by the pump is specified by the manufacturer and is based on the pump design and operating conditions. If the measured NPSH is lower than the required NPSH, it indicates that the pump may experience cavitation and damage the impeller.
NPSH test is crucial because it helps to ensure that the pump is operating under optimal conditions and to prevent damage to the impeller. If the NPSH is not met, steps can be taken to increase the NPSH at the pump suction, such as increasing the suction head, increasing the suction pipe diameter, or lowering the pump or suction pipe. If the NPSH is still not met, it may be necessary to replace the pump with one that has a lower NPSH requirement.
Endurance testing
Endurance testing is a critical method used to test the long-term reliability and durability of pumps. The purpose of endurance testing of pumps is to simulate the conditions that the pump will face during normal operation and identify any potential issues that may arise over time. Endurance testing is essential because it helps to identify potential issues that may not be apparent during short-term testing.
Endurance testing involves running the pump continuously for an extended period, typically for several hours or even days. The pump's performance is continuously monitored and recorded, including flow rate, pressure, power consumption, and vibration levels. This data is used to analyze the pump's behavior under normal operating conditions and identify any trends or issues that may arise over time.
Hydrostatic testing
Hydrostatic testing of pumps is a method used to assess the structural integrity and leak tightness of pump systems. This test involves pressurizing the pump system to a pressure higher than its normal operating pressure to identify any weak points in the system that may fail under high pressure. The purpose of hydrostatic testing is to identify any leaks or weaknesses in the pump system that may not be apparent during normal operation.
During hydrostatic testing, the pump system is filled with a liquid, typically water, and pressurized using a pump or compressor. The pressure is then held for a specified period, typically between 30 minutes to several hours, to allow for a thorough inspection of the system. The pressure applied during hydrostatic testing is typically 1.5 times the normal operating pressure of the pump system.