It is very important to understand the pressure safety valves P&ID arrangement. Because safety valve is one of the most important part in process system. A Pressure Safety Valve (PSV) is a safety device designed to protect a pressure vessel or system from overpressure. The PSV is typically installed in the piping system or vessel and is designed to release excess pressure and prevent the system from rupturing.
Table of content:
Pressure safety valve P&ID arrangement
Guidelines to create P&ID for pressure safety valves
Pressure safety valve P&ID arrangement
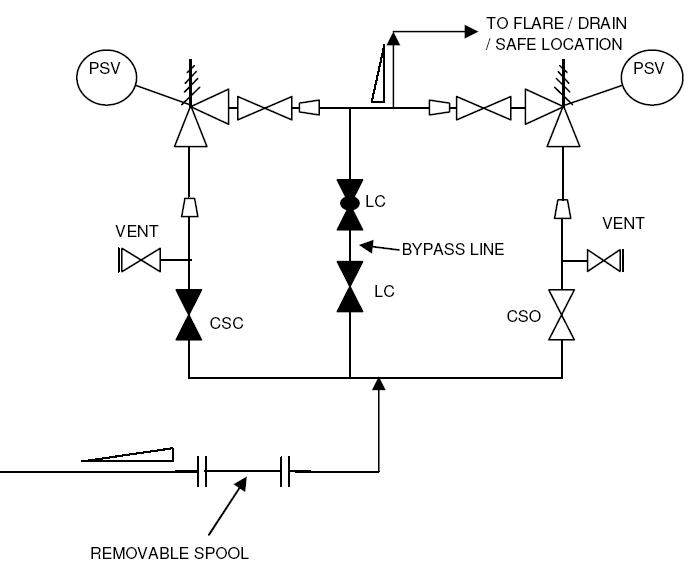
The sample drawing presented here represents a typical arrangement generally used to represent pressure safety valves or relief valves on P&ID.
Guidelines to create a P&ID for Pressure safety valves
Selection of safety valve symbol
The selection of a safety valve symbol in a Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID) of a pressure safety valve (PSV) is important as it conveys important information about the PSV and its function. Therefore a proper safety valve symbol should be selected to represent the control valve as per the project standards.
For protecting equipments that are not spared and equipments that cannot be isolated without disrupting the plant / unit a spare safety valve is recommended to be provided as shown in the sample drawing.
Nozzles
Nozzles are the connection points on the pressure vessel or piping system where the PSV is installed. The PSV is typically installed on the top of the vessel or piping system, and the nozzles connect the PSV to the system.
Generally, the safety valve inlet / outlet nozzles are smaller than the corresponding line sizes. This change in diameter should be clearly indicated in the P&ID with reducer and expander.
Block valve
Block valves should be provided upstream and downstream of the safety valves in case of shutdown and maintenance. Normally provision is made to keep these valves locked or sealed open. The spare safety valve is kept locked or sealed closed, as indicated in the sample drawing.
The block valve is an important component in the P&ID arrangement of a PSV. It allows the PSV to be isolated for maintenance or repair. It also ensures that the pressure vessel or piping system remains protected.
Vent valve
The vent valve is typically used to safely release the excess pressure that has been relieved by the PSV. A vent valve is normally provided between the safety valve and upstream block valve.
Bypass
Normally, bypass should be provided for safety valves for process or start-up requirements. Type, number and size of bypass valves will depend on the project standards.
Discharge
The discharge system is responsible for safely directing the excess fluid or gas that is discharged by the PSV to a safe location. The discharge system should be designed to safely direct the excess fluid or gas to a location where it will not cause harm or damage.
Depending on the service handled, the discharge from PSV can be either routed to flare system for hydrocarbon service, for closed/open drain systems or to atmosphere at a safe location for non-hazardous service.
Inlet / Outlet lines
Inlet and outlet lines ensure that the fluid or gas is safely transported to and from the PSV. The inlet line carries the fluid or gas from the process equipment or piping system to the PSV. The outlet line carries the fluid or gas from the PSV to the discharge system.
The inlet lines to the safety valves are always sloped toward to protected equipment and the outlet lines from the safety valves are always sloped towards the flare header / the knock out drum or the safe location.
Removable pipe spool
The purpose of a removable pipe spool is to allow for easy installation, removal, or maintenance of the PSV without disrupting the rest of the piping system.
When a PSV is connected to the flare system, the inlet line piping should be equipped with a spool piece to facilitate dismantling, as indicated in the sample drawing. For PSVs discharging to atmosphere, this is not required.
All the guidelines given here are very general and may be modified as per specific requirements of any particular project.