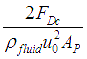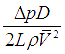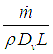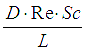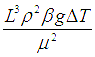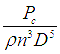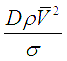Dimensionless numbers are frequently used in fluid mechanics equations. The basis for these dimensionless numbers is often in empirically derived correlations.
| Symbol | Name | Definition | Significance |
| Bi | Biot Number | For a solid body, Biot number is the ratio of convective heat transfer at the surface of the body to conductive heat transfer occurring inside the body. ‘h’ is convective heat transfer coefficient. ‘s’ is characteristic length (volume/surface). ‘k’ is conductivity of the solid body. | |
| CD | Drag coefficient | Drag coefficient characterizes the drag force experienced by a body moving in a fluid. Drag coefficient is a property related to the shape of the moving object. | |
| Fo | Fourier Number | Fourier number is the ratio of heat conduction rate to heat storage rate. ‘ |
|
| Fr | Froude Number | Fraude number is ratio of inertial force to gravitational force. It is a measure for resistance to the motion of a body moving through water. ‘u’ is velocity of the moving object and ‘L’ is characteristic length of that object. | |
| Fanning friction factor | The frictional pressure loss in a pipe is determined by the friction factor which is function of the Reynold’s number for the flow. | ||
| Gz | Graetz Number | Graetz number is useful in determining the thermally developing length in flow ducts. | |
| Gz’ | Graetz Number for mass transfer |
|
Graetz number in mass transfer is useful in determining the diffusively developing length in flow ducts. |
| Gr | Grashof Number | Grashof number is used in fluid mechanics and heat transfer. It is the ratio of buoyancy force to viscous force. It is frequently used in studies of convection. | |
| Ma | Mach Number | Mach number for a moving object is the ratio of speed of that object moving in a fluid (u) to the speed of sound in the fluid (a). | |
| Aeration Number | Aeration number is frequently used for agitated mixing of gas and liquids. |
||
| Power Number | Used often in correlations for agitated mixing of liquids. P is power required to rotate impeller. |
||
| Flow Number | For stirred liquid vessels |
||
| Nu | Nusselt Number | In case of heat transfer occurring at the surface of a fluid, Nusselt number is the ratio of convective heat transfer to the conductive heat transfer occurring at the liquid surface. ‘h’ is convective heat transfer coefficient, ‘D’ characteristic length and k is the conductivity of fluid. | |
| Pe | Peclet Number |
or |
Peclet number is defined to be the ratio of mass transfer occurring by advection to the mass transfer occurring by diffusion. For heat transfer, Peclet number is product of Re and Pr. For mass transfer, Peclet number is product of Re and Sc.
Here ‘D’ is characteristic length, |
| Pr | Prandtl Number | Prandtl number is essentially the ratio of kinematic viscosity |
|
| Re | Reynolds Number | Reynolds number is ratio of the inertial forces in a flowing fluid to the viscous forces acting on the fluid. | |
| Sc | Schmidt Number | Similar to the Prandtl number for heat transfer, Schmidt number in mass transfer is the ratio of kinrmatic viscosity |
|
| Sh | Sherwood Number | Sherwood number is the mass transfer equivalent of Nusselt number from heat transfer. It is the ratio of convective mass transfer to diffusive mass transfer at the phase boundary surface. |
|
| We | Weber Number | It is the ratio of inertial forces acting on the fluid to the surface tension acting forces. ‘D’ is characteristic length, |