A Sulphur Recovery Unit (SRU) is a plant used to recover sulphur from hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas, which is commonly found in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants. The sulphur recovery unit uses a series of chemical and physical processes to convert H2S into elemental sulphur, which can then be used in a variety of industrial applications.
Table of content:
1. Sulphur recovery process
2. Sulphur Recovery Unit
Sulphur recovery process
Sulphur recovery is the process of converting hydrogen sulphide (H2S) gas into elemental sulphur. The process is commonly used in oil and gas refining, natural gas processing, and other industrial applications to remove toxic H2S from process streams and to produce valuable sulphur as a byproduct.
The sulphur recovery process typically involves several stages, including:
- Claus process: This is the most widely used process for sulphur recovery. In this process, H2S gas is burned with air to form sulphur dioxide (SO2) gas. The SO2 gas is then reacted with additional H2S in a series of catalytic reactors to form elemental sulphur.
- Tail gas treatment: The Claus process typically produces a gas stream containing residual H2S and SO2, called tail gas. The tail gas is then treated in a series of additional reactors to convert the remaining H2S and SO2 into elemental sulphur and/or sulphuric acid.
- The final stage of the sulphur recovery process involves removing the elemental sulphur from the process stream and preparing it for sale or storage.
Sulphur Recovery Unit
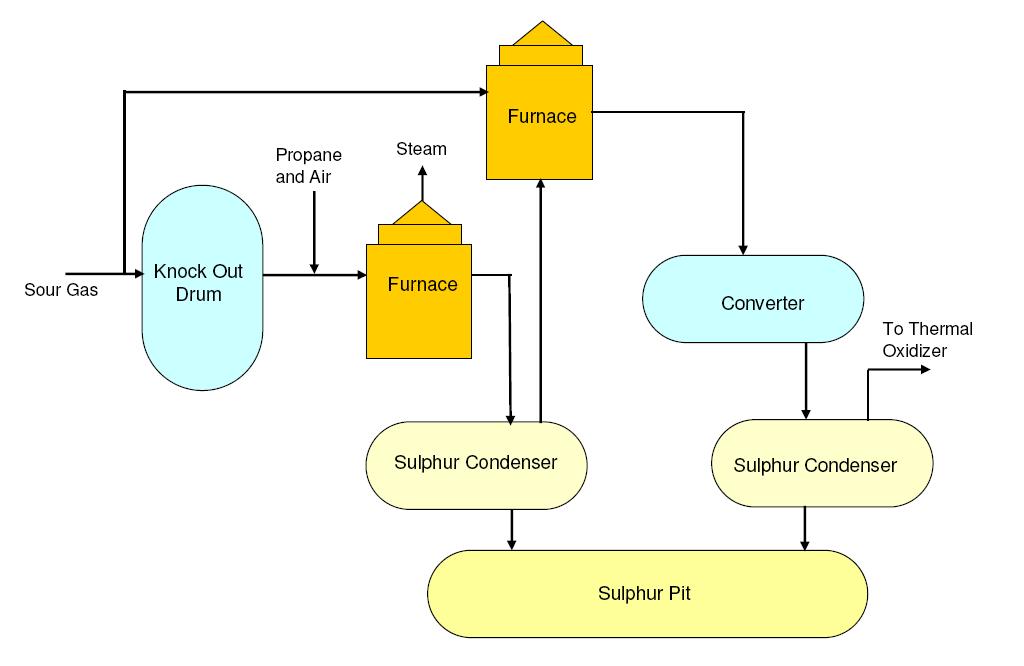
Usually crude oil extracted from geological sources is accompanied by hydrogen sulphide gas (H2S). This H2S is separated from rest of the oil at the atmospheric distillation unit along with lighter hydrocarbons and collectively termed as 'sour gas'. H2S is separated from hydrocarbons at the amine treatment unit and H2S rich gas flow is sent to sulphur recovery unit (SRU) for extracting elemental sulphur from H2S gas.
The basic process used in sulphur recovery unit (SRU) is 'Claus Process' which involves combustion of a part of H2S gas to form SO2. Later this SO2 is reacted (conversion) with H2S in presence of catalyst (Cobalt / molybdenum / aluminum oxide ) to form elemental sulphur and steam.
The main chemical reactions involved are:
2H2S + 3O2 → 2SO2 + 2H2O (Combustion reaction)
4H2S + 2SO2 → 6S + 4H2O (Conversion reaction)
Note that around one third of the H2S is first combusted and then reacted with rest of the H2S to give elemental sulphur and steam as end products.
Generally upto 97% of H2S to elemental sulphur is achievable with the use of multiple conversion reactors. If the remaining H2S has to be removed from the tail gas due to environmental concerns, the remaining tail gas can be sent to a Tail Gas Treatment (TGT) absorber.