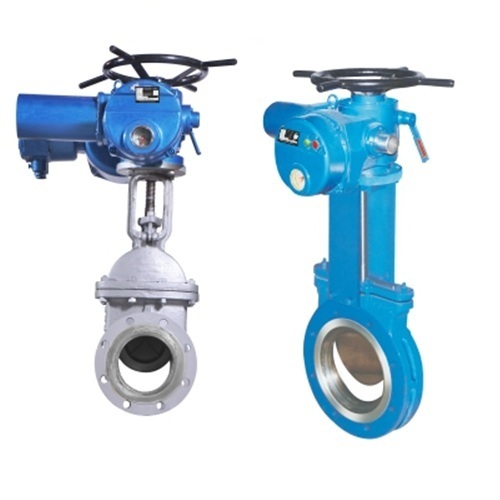
A gate valve is a type of valve that is used to control the flow of fluid through a pipe. It is named after the gate like mechanism inside the valve that either allows or blocks the flow of the fluid. In this post, we will explore the structure of a gate valve and how they function along with their applications across various industries.
Table of content:
1. What is a Gate Valve?
2. How Does a Gate Valve Works?
3. Parts of Gate Valve
4. Types of Gate Valves
5. Advantages
6. Disadvantages
7. Applications of Gate Valves
What is a Gate Valve?
Gate valves are a type of control valve that uses a flat or tapered disc to control the flow of fluid. Gate valves are named after the gate that they use to control the flow of fluid. The gate is a flat or tapered disc that slides vertically in and out of the path of the flow. The gate is typically made of a strong material, such as steel or stainless steel. It is attached to a stem, which is turned by a handwheel or actuator. When the handwheel is turned, the stem turns, which moves the gate in or out of the path of the fluid. When the gate is in open position fluid can flow freely and when the gate is in closed position fluid is blocked.
Gate valves are typically used to isolate sections of a piping system for maintenance or repair. They can also be used to control the flow of fluid in a system. Gate valves are not typically used to throttle the flow of fluid, as they can create a large amount of pressure drop when the gate is partially closed.
Large gate valves can be difficult to operate manually. The force or torque required to operate the handwheel can be significant. For this reason, large gate valves are often operated with automatic actuators. Automatic actuators can be pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic.
How Does a Gate Valve Works?
Gate valves work by using a gate or barrier mechanism to control the flow of fluid through a pipe.
Fully Open Position: When the gate valve is fully open, the gate is lifted or retracted completely into the bonnet. This creates a straight, unobstructed flow path through the valve. The fluid can flow freely through the valve with minimal resistance, allowing for maximum flow capacity.
Partially Open Position: To begin closing the gate valve, the wheel-like handle or actuator is turned in the opposite direction. As the handle or actuator is rotated, the gate starts moving downwards, partially obstructing the flow path. The degree of closure can be adjusted to regulate the flow to a desired level, although gate valves are not typically used for precise flow control.
Fully Closed Position: When the gate valve is fully closed, the gate is lowered or extended fully, completely blocking the flow path. The gate makes contact with the seating surfaces on the body, forming a tight seal to prevent any fluid from passing through. In the closed position, gate valves provide a high degree of sealing, minimizing leakage.
It's important to note that gate valves are typically operated in a fully open or fully closed position. The gate itself is not designed for partial opening or fine adjustments.
The operation of a gate valve can be manual, where the handle is manually turned to open or close the valve, or it can be automated with the use of electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuators.
Parts of Gate valve
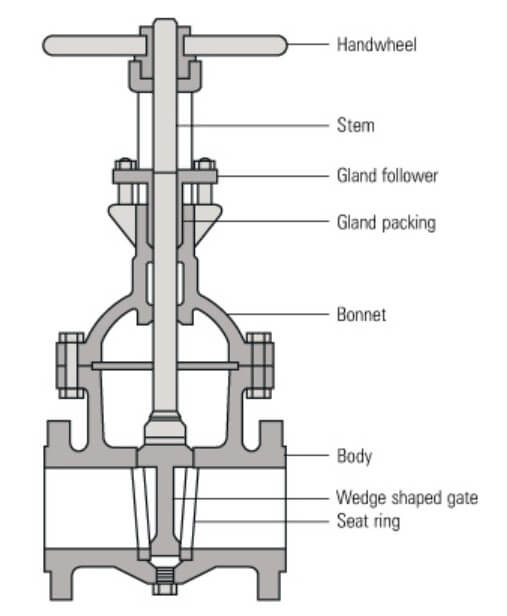
A gate valve is a type of valve used to control the flow of fluids. It consists of several parts that work together to regulate the fluid flow. The main components of a gate valve include:
Body: The body of the gate valve is the outer shell that houses all the internal components. It provides structural integrity and serves as the main connection point to the pipeline.
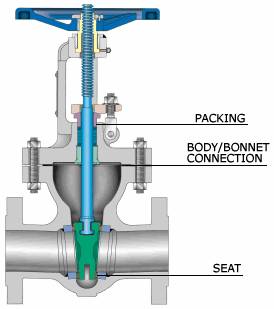
Bonnet: The bonnet is the cover on top of the valve body. It provides a protective enclosure for the stem and other internal parts. It is typically bolted or threaded onto the valve body.
Gate: The gate is a flat or wedge-shaped component that controls the flow of the fluid. It moves up and down to either block or allow the fluid to pass through the valve. The gate is usually made of metal and is connected to the stem.
Stem: The stem is a vertical rod that connects the gate to the actuator (handle, wheel, or motor) outside the valve. It transfers the motion from the actuator to the gate, allowing it to open or close.
Seat: The seat is the sealing surface located on both sides of the gate. When the gate is fully closed, it makes contact with the seats, creating a tight seal to prevent any fluid leakage.
Wedge guides: In the case of a wedge-shaped gate, there are wedge guides or guides on the sides of the gate. These guides ensure proper alignment and stability of the gate during operation.
Packing: The packing is a sealing material that prevents leakage along the stem. It is usually made of flexible material, such as graphite or PTFE, and is compressed around the stem to create a seal.
Gland: The gland is a compression device that holds the packing in place and allows for adjustment or replacement of the packing if needed. It is usually located above the bonnet and is tightened to maintain the desired compression on the packing.
Stem nut: The stem nut is a threaded component that connects the stem to the actuator. It converts the rotary motion of the actuator into linear motion of the stem, allowing the gate to move up or down.
Backseat: The backseat is a secondary seating surface located at the top end of the stem. When the valve is fully open, the gate makes contact with the backseat, providing additional sealing and support.
Types of Gate Valves
Gate valves can be classified into different categories based on the type and design of closing element and the type of stem. In the following section we will study classification of gate valves based on the type of closing element.
1. Solid Wedge Gate Valves
These gate valves have a solid, one-piece disc or wedge. These valves are used in applications where the pressure does not fluctuate significantly and the flow rate does not need to be adjusted regularly.
- Solid wedge gate valves require less maintenance than other types of gate valves as they have no moving parts.
- They also provide better sealing capabilities than other types of gate valves due to less moving parts.
- However, these valves cannot be adjusted once they have been installed and may not be suitable for applications where the pressure fluctuates significantly or the flow rate needs to be adjusted regularly.
- This type of gate valves are known for their robustness and durability, making them suitable for handling various fluids, including those containing solids or slurries.
2. Flexible Wedge Gate Valves
In flexible wedge gate valves, the disc or wedge is divided into multiple segments that can adjust and adapt to changes in the seating surfaces. This design allows for better sealing in applications where thermal expansion or contraction of the valve components may occur.
3. Split Wedge Gate Valves
Split wedge gate valves have a disc or wedge that is split into two halves. The split design allows the gate to expand and contract independently, reducing the possibility of binding due to thermal effects. This type of gate valve is often used in high-temperature applications.
4. Parallel Slide Gate Valves
Parallel slide gate valves have parallel sliding discs or gates that move in a linear motion. This design offers better sealing capabilities compared to other gate valve types and is often used in applications where tight shut-off is required.
5. Double Disc Gate Valves
Double disc gate valves, also known as dual disc gate valves, are a type of gate valve that feature two parallel discs or gates that move in opposite directions to control the flow of fluids. In these valves the gate is formed by two discs which are forced apart by springs. This design allows for bidirectional flow control. These valves are commonly used in applications where high flow capacity, low pressure drop, and reliable sealing are required. These discs provide tight sealing against parallel seats.
6. Bellows Seal Gate Valves
Bellows seal gate valves are specifically designed to minimize the leakage of hazardous fluids to the environment through the valve stem. These valves incorporate a metallic bellows assembly between the valve stem and the bonnet to provide a reliable and effective sealing mechanism.
The purpose of using a bellows assembly in these valves is to prevent the escape of harmful fluids or gases from the valve stem area. The metallic bellows acts as a dynamic seal, accommodating the linear motion of the stem while maintaining a leak-tight barrier. It effectively isolates the process fluid from the external environment, reducing the risk of leakage and preventing the release of hazardous substances.
Advantages
When the valve is fully open, the pressure drop across a gate valve is very low. These valves can be used for bidirectional action. They are very handy as on-off valves.
Here are the advantages of gate valves.
- They are reliable for complete shut-off or full flow control. This makes them handy as on-off valves.
- Bi-Directional Flow: Gate valves can handle flow in both directions. Because of that these valves can be used for bidirectional action.
- Wide Range of Sizes: Available in various sizes, gate valves offer flexibility for different system requirements.
- Suitable for High Pressure and Temperature: Gate valves can withstand challenging conditions, making them suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- When the valve is fully open, the pressure drop across a gate valve is very low.
Disadvantages
- Gate valves are primarily designed for on/off applications and are not well-suited for precise flow regulation.
- Gate valves need a large force to for operation and large sized valves require automatic actuators.
- Gate valves are not very quick to open or close compared to some other valves.
- They take up more space compared to other valves.
- For some valves facing high temperature fluctuations, thermal expansion and shrinking can lead to unwanted leakage.
Applications of Gate Valves
- Applications as shut-off valves
- Socket or butt-welding end valves for several services
- Threaded end valve for gaseous or liquid systems
- Water distribution, fire water systems operating at low pressures