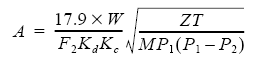Pressure relief valves are critical components in many industrial processes. Subcritical gas flow refers to the flow of gas at pressures and temperatures below their critical points, where the gas remains in a gas phase rather than condensing into a liquid.
PRVs are installed to prevent such situations and to automatically relieve excess pressure by opening when the pressure inside the system reaches a predetermined setpoint. Proper sizing of pressure relief valves is crucial for their effective operation in subcritical gas flow systems.
Table of content:
Subcritical gas flow
Pressure relief valve sizing calculation for subcritical gas flow
Problem Statement
Design a pressure relief valve for the following service.
Protected equipment : Separator vessel
Relief service : Fuel Gas
Reason for relief : Blocked gas discharge
Relieving Rate : 10,000 kg/hr
Gas Density : 4.1 kg/m3
Ratio of specific heats for the gas (CP/CV) : 1.55
Compressibility factor of gas = 0.95
Molecular weight of gas = 20 gm/mole
Relieving temperature = 200C
Set pressure : 4.5 barg
Accumulation : 10%
Back pressure at relief valve discharge : 2.1 barg
Type of relief valve : Balanced Bellows
Solution
This sample problem for relief valve sizing calculation can be solved in following steps, which are based on pressure relief valve sizing procedures described in API RP 520 Part I. The first step is to determine whether the gas flow type is critical or sub-critical.
Step1
The first step is to determine if the flow conditions are critical or sub-critical. For this purpose the critical flow pressure (Pcf) downstream to the relief valve has to be calculated using the following equation from API RP 520 Part I,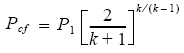
P1 : Relieving pressure upstream to relief valve in bara
P1 = 5.96 bara (including 10% accumulation)
k : Ratio of specific heats of the gas .. (CP/CV)
k = 1.55
Pcf : Critical flow pressure for the given flow conditions in bara
Pcf = 3.0 bara
If the pressure downstream or back pressure (3.113 bara) of the relief valve is greater than the critical flow pressure (3.0 bara), then the flow is said to be of sub-critical type. In the present case, back pressure (3.113 bara) > Pcf (3.0 bara). Hence the flow is of sub-critical type.
Step2
Next step is to use the relief valve sizing procedure given in the API 520 part I for sub-critical flow type gas relief valve. The following equation is used,
... (1)
A : orifice are requirement in mm2
W : flowrate in kg/hr
W = 10,000 kg/hr
T : Temperature in Kelvin
T = 273.16 + 20 = 293.26 K
Z : compressibility factor of gas
Z = 0.95
M : Molecular weight of the gas
M = 20 gm/mole
P1 : Relieving pressure upstream to relief valve in bara
P1 = 5.96 bara (including 10% accumulation)
P2 : back pressure downstream to relief valve in bara
P2 = 3.11 bara
Kd : Coefficient of discharge
Kd = 0.975 for gas service
KC : combination correction factor for use of rupture discs
KC = 1 (for absence of rupture disc upstream to the valve)
F2 : Coefficient of sub-critical flow
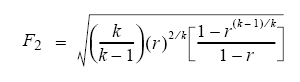
k : Ratio of specific heats of the gas .. (CP/CV)
k = 1.55
r : ratio of back pressure to relieving pressure
r = P2/P1 = 0.58
hence, F2 = 0.5985
Plugging this data into equation (1), the minimum required orifice area for the relief valve is calculated to be,
A = 34.07 cm2
Step3
The next higher available orifice area should be selected for the pressure relief valve to be actually installed.
- Referring to the table of standard orifice sizes given in EnggCyclopedia's relief valve sizing calculator, next high available orifice area is selected to be A = 41.20 cm2 and the corresponding designating letter is 'P'.
- Available valve size is '4P6', which corresponds to different nozzle sizes for suction and discharge nozzles of the pressure relief valve. For a '4P6' valve suction nozzle is of 4" size and discharge nozzle of 6" size.