NFPA standards from National Fire Protection Association provide guidelines for incorporating fire protection safety measures in industrial systems.
Classification of Fire and Hazard as per NFPA - The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) categorizes fires by class. A fire can be classified among these classes - Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D and Class K. In accordance with NFPA, areas are typically classified as being light (low) hazard, ordinary (moderate) hazard, or extra (high) hazard.
Fire Extinguishers – color codes and symbolic representation – In accordance with NFPA 10 (2007 edition), the selection of fire extinguishers depends mainly on the following parameters: (i) type and size of fire most likely to occur, (ii) present hazards in the area where the fire is most likely to occur, (iii) existence of electrical equipment in close proximity to the area where the fire will most probably occur, (iv) ambient temperature conditions, (v) other conditions, such as human presence in the area where the fire is most likely to occur, whether the suspect area is ventilated or not etc.
Fire Hydrants – In accordance with NFPA 25, a fire hydrant is a valved connection on a water main having as a purpose to supply water to various fire protection apparatus, fire hose or other. There are four (4) major types of hydrants mainly in use nowadays: (i) Dry Barrel type fire hydrant (ii) Monitor Nozzle fire hydrant (iii) Wall fire hydrant (iv) Wet barrel fire hydrant
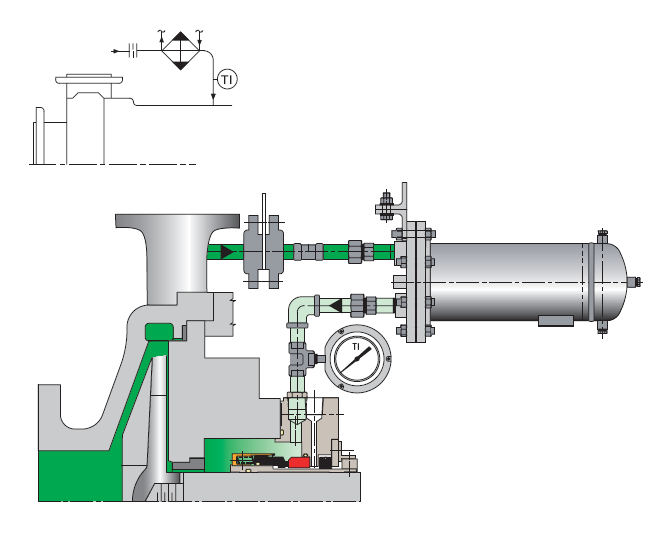
Fire Fighting Pumps (centrifugal type) – In accordance with NFPA 20 (2007 edition), fire fighting pumps - shall be specifically dedicated and listed for fire protection service. Electric motors, diesel engines or even steam turbines (for big pumps) are the acceptable drivers for fire fighting pumps.A fire fighting pump set is selected typically from the following types of pumps:
- One (1) 100% motor-driven pump
- One (1) 100% diesel-driven pump for redundancy reasons
- One (1) jockey or make up pump, usually of vertical type. Jockey pumps are pressure maintenance pumps and their basic role is to cover the various pressure losses of fire fighting network.
Fire protection for power generation plants – NFPA 850 provides recommendations (not requirements) for fire protection for fossil fueled (i.e. coal, gas or oil) or alternative fueled (i.e. biomass, solid waste etc) power generation plants. Nuclear power plants or hydroelectric power plants are not covered by NFPA 850: Nuclear power plants standards are addressed by NFPA 805, whereas recommendations for hydroelectric power plants are presented at NFPA 851.