Gasification Process
Gasification is a process of converting carbonaceous fuel into gaseous product with a usable heating value. Carbonaceous fuels such as coal, biomass, residual oils and natural gas. Gasification of coal or biomass is usually used to produce an easy to use fuel gas.
Gasification is not done in a single step, but involves multiple sub processes and reactions. The generated Synthesis Gas or ‘Syn Gas’ has wide range of applications ranging from direct house hold applications to power generation. Of all gasification processes, coal gasification has gained much interest from last three decades. Coal can be gasified by reacting it with mixture of air and steam at various temperature and pressure conditions. Biomass gasification is also gaining attention in recent times as it represents an attractive sustainable energy alternative.
Gasification Reactions
There are several stages and corresponding reactions involved in gasification - Drying of fuel, Devolatalization, Oxidation of char and Reduction in absence of oxygen. Syn-gas is produced at the end of the reduction subprocess in the gasifier. All these substeps generally take place in different zones of the gasifier, depending on the type of gasifier used.
Fuels
Characteristics of various gasification fuels are important in selection of gasifier. Different carbon based fuels like - coal, biomass, waste materials, residual oil etc. can be gasified to a syn gas. Suitability of these fuels for syn gas generation by gasifiction process depends on these characteristics such as - ash content, heating value, voidage etc.
This post goes deeper into a discussion of these characteristics and how they are important.
Products
Synthesis gas or syngas is the primary product of gasification. Main constituents of syngas are carbon monoxide and hydrogen. If the syngas contains some non-combustible gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen, the mixture is commonly known as producer gas. If the generated synthesis gas contains only carbon monoxide and hydrogen, then the mixture is known as water gas. Water gas is commonly used for producing pure hydrogen for fuel cell applications, hence purity of the carbon monoxide and hydrogen mixture is important for water gas.
Syngas, producer gas and water gas are useful for quite a few applications -
Syngas applications
- Intermediate in the industrial synthesis of hydrogen and ammonia.
- Syngas has 50% of the energy density of natural gas.
- It can be burnt and is used as a fuel source.
- Used as a fuel in power generation using IGCC power plant.
Producer gas applications
- Fuel for hot-air generators used to produce hot air in production of fertilizer and cement.
- Used for heating water in a number of industrial applications.
- Suitable for melting glass in the production of artifacts.
- Used in food processing to provide heat for drying vegetables, seeds and to heat ovens in bakeries.
Water gas applications
- Used as a feed to gas turbines in power generation.
- Primarily water gas is used for hydrogen production using water gas shift reaction also known as Lowe's Process. Water gas shift reaction (Lowe's gas Process) CO+H2O → CO2+H2 is used to remove carbon monoxide from water gas to get pure hydrogen for the fuel cell applications.
Gasification Types
Gasification processes can be categorized into three groups: entrained flow, fluidised bed and moving bed. These processes differ from each other on account of fuel particle size, residence time in the gasifier and operating temperatures. Due to these differences, composition of the product gases and percent conversion of coal is also different for each process. When selecting a specific gasification process for syn gas generation, different factors such as fuel type (coal or biomass etc.), plant size, reactivity of fuel and composition of air-oxygen oxidant mixture have to be taken into consideration.
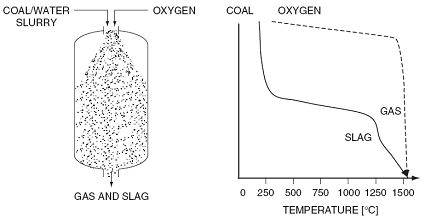
Entrained flow
In entrained bed type gasification process, feed and oxygen enter in co-current flow.
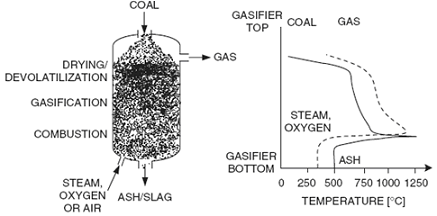
Fluidized bed
Fluidized bed gasification offers good mixing of coal and air/oxygen and steam mixture, which promotes both heat and mass transfer. This ensures an even distribution of material in the bed and hence, a certain amount of partially reacted fuel is inevitably removed with the ash.
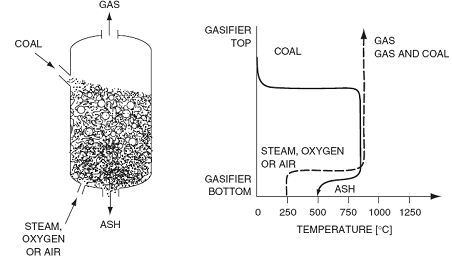
Moving bed
In this gasifier, the hot synthesis gas from gasification zone is used to preheat and pyrolyze the downward flowing coal.
Gasifier types are different than the types of gasification processes. Gasifiers are classified as upward draft, downward draft and cross draft gasifiers, based on the direction of air/oxygen flow in the equipment. The selection of a gasifier type is mostly determined by factors such as - fuel, its final available form, its size , moisture content and ash content.
The first three gasifier types are mostly used in entrained bed gasification process and moving bed gasification process. While the last one (fluidized bed gasifier) is used for fluidised bed gasification.
For selecting a specific gasification process and gasifier following factors are evaluated - characteristics of coal or biomass used (such as particle size, ash content), reactivity of the fuel, type and composition of the oxidant (air/oxygen), plant size.
Coal gasification
Coal is one of the widely used fuels for gasification. Hence, it is important to analyse different coal samples to check their suitability as a gasification fuel. The main purpose of coal analysis is to determine the rank of the coal based on its intrinsic characteristics.
For different types of coal, following properties are important in analysis - moisture, volatile matter content, ash content, fixed carbon content. Different analysis techniques such as proximate coal analysis, ultimate coal analysis, ash analysis are used for coal sample analysis for gasification purpose.