Pigging is the process of using a device called a pig to clean, inspect, or remove debris from a pipeline. Pigs are typically made of metal or plastic and are inserted into the pipeline at one end and forced through the pipeline by pressure. As the pig travels through the pipeline, it can remove debris, clean the walls of the pipeline, or collect data about the condition of the pipeline.
Pigging is a valuable tool for maintaining the integrity of pipelines. It can help to prevent blockages, corrosion, and leaks. Pigging can also be used to collect data about the condition of the pipeline, which can be used to identify potential problems before they cause a failure.
Table of Content:
1. What is Pipeline Pigging?
2. Importance of Pipeline Pigging
3. What is pigging in oil and gas pipelines?
What is Pipeline Pigging?
Pigging refers to maintenance practice for pipelines using 'pipeline pigs', for cleaning or inspection of pipeline without stopping operation of the pipeline. Pipeline pigs are capsule shaped objects which travel through the pipeline, cleaning the inner walls of the pipeline by brushing action. Pigs get their name from the squealing sound they make while traveling through a pipeline.
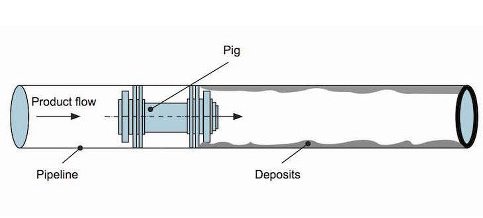
The pig is inserted into a pig launcher, which is essentially a vessel used for launching the pig into a pipeline by creating a differential pressure. The differential pressure between the two ends of pig launcher is created by partially closing the bypass line on the pig launcher. After launching the pig into the pipeline, pig launcher is closed and the fluid pressure is then used to push this pig through entire length of the pipeline, cleaning the inner walls all the way to the other end.
On the other end of the pipeline, this pipe pig is received by a pig receiver, which has a similar structure and arrangement as the pig receiver. After receiving the pipe pig, pig receiver is closed, depressurized and then pig is removed along with the dirt and sludge.
If the pipeline contains butterfly valves, the pipeline cannot be pigged. Full bore ball valves cause no problems because the inside diameter of the ball can be specified to be the same as that of the pipe.
Importance of Pipeline Pigging

Pipelines are the lifelines of various industries, enabling the transportation of liquids, gases, and other products over long distances. However, these vital arteries require regular maintenance to ensure their smooth functioning and prevent issues that can disrupt operations.
Over time, pipelines can accumulate debris, sediment, scale, and other contaminants that hinder the flow of products, reduce efficiency, and even pose safety risks. Corrosion, cracks, and leaks are also common issues that need to be addressed promptly to prevent environmental damage and financial losses. This is where pigging comes into play.
Pigging plays a crucial role in ensuring efficient pipeline operations and mitigating potential problems. By employing pigs, companies can effectively clean the pipelines, remove unwanted deposits, and inspect the integrity of the walls. This proactive maintenance approach helps prevent blockages, optimize flow rates, minimize product contamination, and extend the lifespan of pipelines. Furthermore, regular pigging enhances safety by identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate into catastrophic failures.
Here are some of the major benefits of pigging:
- Improves pipeline efficiency by removing debris and contaminants that can clog the pipeline and reduce flow.
- Reduces the risk of leaks by removing debris that can cause corrosion and cracks.
- Extends the life of the pipeline by preventing corrosion and other damage.
- Improves safety by reducing the risk of explosions and fires.
- Saves money on repairs and replacements by preventing leaks and other problems.
Pipe pigging can be used for almost any section of the transfer process between, for example, blending, storage or filling systems. Pigging systems are already installed in industries handling products as diverse as lubricating oils, paints, chemicals, toiletries, cosmetics and foodstuffs.
What is pigging in oil and gas pipelines?
In oil and gas pipelines, pigging refers to the practice of using pipeline inspection gauges, to clean, inspect, and maintain the pipelines. Pipe pigs are very frequently used in oil and gas pipelines to clean the pipes. Also there are "smart pigs" used to measure things like pipe thickness and corrosion along the pipeline. They usually do not interrupt production, though some product can be lost when the pig is extracted. They can also be used to separate different products in a multiproduct pipeline.

Pigging operations are essential for the safe and efficient operation of oil and gas pipelines. They help ensure the integrity of the pipelines, extend their lifespan, and reduce the risk of accidents or disruptions in the flow of products. Regular pigging is typically performed as part of a pipeline maintenance program, with the frequency determined by factors such as pipeline length, product characteristics, and operational requirements.
Pigs are used to remove debris, sediment, wax, scale, and other build-ups from the inside walls of the pipeline. By passing a cleaning pig through the pipeline, it scrapes off or brushes away accumulated materials, helping to maintain the pipeline's efficiency and preventing blockages.
Intelligent pigs, also known as inline inspection (ILI) tools, are equipped with various sensors and instruments that assess the condition of the pipeline. These pigs collect data on wall thickness, corrosion, cracks, weld defects, and other anomalies. The information gathered helps identify areas that require repair or further inspection.
Pigs can also be used for maintenance activities, such as applying coatings or inhibitors to protect the pipeline against corrosion. Additionally, they can be used for pipeline displacement, where pigs are used to displace one product with another, or to remove residual product from the pipeline.
Check these related posts for more detailed understanding of pipeline pigging.
Pipeline Pigging Procedure
Check the given post to study Hazards involved in the pigging operations, precautions to be taken during pigging and typical step by step procedure for pigging. The procedures to be followed at pig launcher end and at pig receiver end are also discussed.
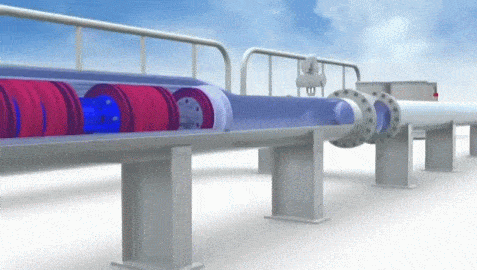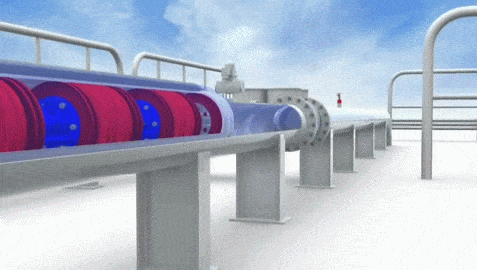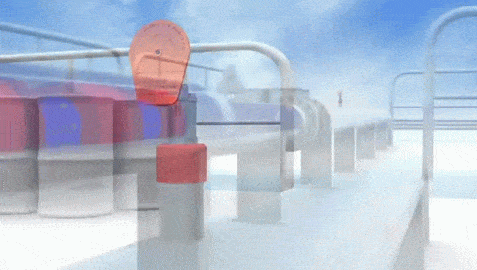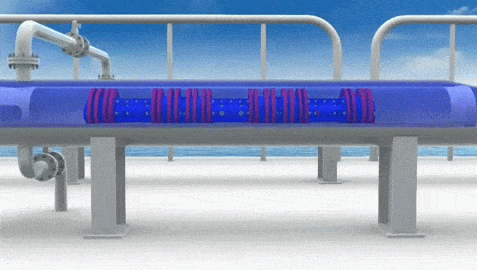

Pipeline Pig Types
There are several types of pipe pigs, each designed for a specific purpose. The type of pig to be used and its optimum configuration for a particular task depends on the purpose of pigging, contents in the pipeline, and characteristics of the pipeline such as size, minimum bend radius, types of valves etc. Based on these factors a type of pig tool is chosen. Check detailed discussion on types of pipe pigs in the given post.
Pig Traps (pig receivers and pig launchers)
Pig traps (pig receivers, and pig launchers) are devices used in pipeline pigging to safely and effectively transport pigs through pipelines. They help to prevent pigs from getting lost or damaged, and they improve the efficiency of the pigging process.