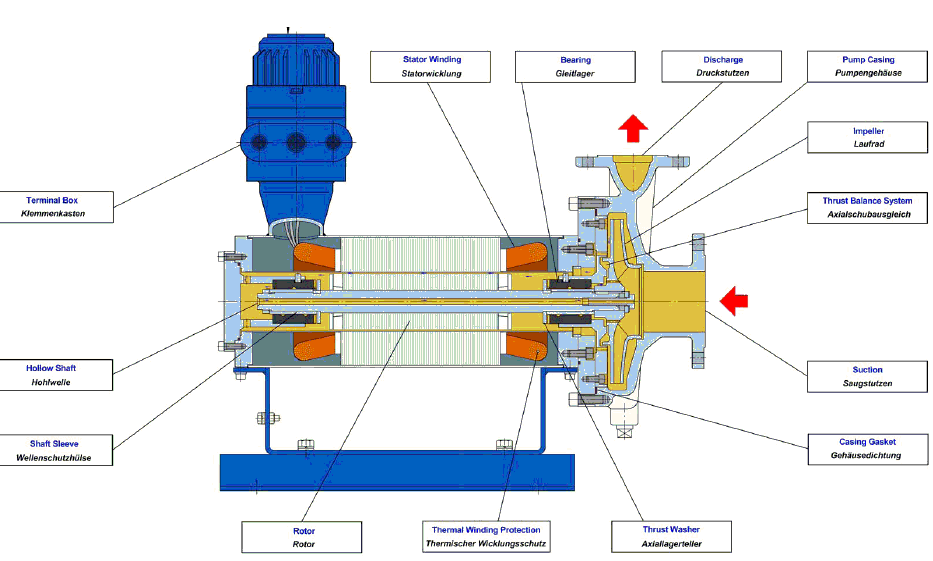
Canned pumps, also known as canned motor pumps or integrated motor pumps, are a type of centrifugal pump with a unique design that combines the pump and motor into a single unit. The motor and pump components are enclosed within a sealed casing, hence the term "canned." This design eliminates the need for a separate motor shaft, coupling, and mechanical seal, resulting in a more compact and efficient system.
Table of Content:
1. Canned Motor Pump
2. Canned Motor Pump Start-up Procedure
2.1. Preparation of canned motor pump for start-up
2.2. Canned motor pump start-up procedure
Canned Motor Pump
Canned motor pumps (CMPs) are a type of sealless pump that combines a centrifugal pump and a squirrel cage induction motor into a single sealed unit. The pump liquid is allowed to recirculate through the rotor cavity to cool the motor and lubricate the bearings.
Canned motor pumps are developed to eliminate liquid leakage to the atmosphere. This leakage is usually toxic or dangerous to the environment or very expensive. Canned pumps are used in applications where liquid leakage to the atmosphere is not desired, such as in the chemical and petrochemical industries.
Here are some of the key features of canned motor pumps:
- Sealed motor: The motor is sealed inside the pump, so there is no possibility of liquid leakage to the atmosphere.
- Leak-proof: Canned motor pumps are leak-proof, which eliminates the risk of contamination and environmental damage.
- Efficient: These pumps are very efficient, which can save energy and money.
- Reliable: These pumps are very reliable and have a long service life.
- Quieter Operation: The integrated motor design of canned pumps reduces noise and vibration levels. The absence of a shaft and coupling eliminates the source of many noise-related issues in conventional pumps.
Here are some of the disadvantages of using Canned motor pumps:
- Expensive: Canned pumps are more expensive than traditional pumps.
- Not versatile: These pumps are not as versatile as traditional pumps, and they may not be suitable for all applications.

Check how canned motor pumps work and what makes them so dependable in the given post.
Canned Motor Pump Start-up Procedure
Preparation of canned motor pump for start-up
Never start up the pump without pumping medium! This will lead in all cases to destruction of the slide bearings.
- If the pump is to be cooled or heated, open the corresponding stop valves and regulate the flow; allow the steady-state temperature to be reached in heated pumps. If monitoring equipment is used, adjust the monitoring equipment. The shutdown temperature of the temperature probe depends on the operating temperature of the pumping medium, and it should be 10 to 15°C higher than this temperature.
- Correct priming and venting of canned motor pumps are essential for proper operation and pump start-up.
- Open the stop valves on the suction side in the by-pass lines.
- If the pump is vented to the discharge line then open the stop valve on the discharge side completely once, and then closed almost completely again before pump startup.
- If the pump cannot be vented into the discharge line, for example if a non-return valve is used or if other pumps are already operating in the same discharge line, the pump must be vented by means of a separate air bleed cock on the discharge side or the by-pass line.
- When liquids are pumped which form gases or vapor which must not escape, the pump is vented into the suction vessel through piping which can be sealed off.
Canned motor pump start-up procedure
- Close the priming and venting lines.
- Open the valve in the discharge line slightly.
- Open the valve in the inlet/suction line completely.
- Start the motor.
- Check the direction of rotation of the canned pump. To check direction of rotation: If the canned pump does not reach the required discharge head as listed in the technical specifications and it has been ensured that all air or gas has been removed from the pump (by starting again if necessary), the pump is operating in the wrong direction. In this case, change the phase sequence of the power supply and check discharge head.
- When the manometer indicates pressure, open the discharge gate valve until operating pressure has been attained.
Attention! The pump should operate for only short periods when the discharge gate valve is closed (excessive heating).
7. The pump flow and power requirement of the pump increases with decreasing discharge head.