Different types of steam
Steam is generated by simply boiling water. But depending on the gas-vapor content of the steam and its temperature above the boiling point, we can define different types of steam for practical usage.
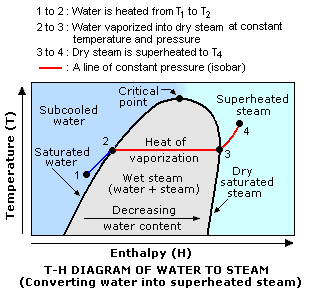
Steam T-H diagram (Temperature Vs Enthalpy) depicts the phase change of:
liquid water (1) -> boiling water (wet steam) (2-3) -> dry steam -> superheated steam (4)
Wet steam
As the name suggests, wet steam has water content along with the gaseous steam. For this reason the wet steam is at its boiling point. Any heat that is added to wet steam will be first used for boiling off remaining liquid water before the steam temperature can be raised.
Steam quality is defined as the percentage gaseous content within the wet steam mixture. This is an important parameter to define the exact thermodynamic state of the steam mixture. Steam with more liquid content is then considered to be of lesser quality.
Dry steam
As per the name, there is no liquid water content in the dry steam. Since every water molecule is in vapor form, the quality of dry steam can be said to be of 100%.
Dry steam can be at or above the boiling point of the steam at given pressure.
Superheated steam
Superheated steam also has 0 liquid content. In fact, steam is said to be superheated when it is heated above its boiling point temperature. This way additional heat supplied is raised by gas molecules for temperature raise.
Generally superheated steam is generated at the boilers to be used in many applications as a utility, wherever you want to avoid two phase flow in the steam network pipes.
Whenever dry steam at the boiling point is needed, a steam desuperheater can be used to bring down the steam temperature at around 3 deg C above the boiling point.
Industrial applications of steam
Industrial applications of steam systems such as - steam tracing, steam blowing, steam hammering etc. Check out resources on industrial steam systems.
Steam Blowing - Cleaning by steam blowing is carried out essentially for steam circuits (i.e for steam generating boilers, steam heated exchangers, steam turbine upstream piping or other steam lines). Due to problems of condensation of steam or draining of condensate, this type of cleaning has to be used with the utmost care, as it can potentially create vacuum in the equipments being cleaned.
Steam generating boilers - Boilers are basically vessels used for heating the water and converting it to steam, as the name suggests. Boilers vessels generally use an internal heat source for boiling the water. Generally the steam is used as a utility in process plants and needs to be available at certain temperature and pressure conditions. A boiler is designed based on the desired temperature pressure conditions of the product steam.
Steam hammering - Steam hammering is the phenomenon which occurs in steam charging in the pipeline while there is a presence of condensate in the line. This is because of sudden drop in pressure of steam as it comes in contact of condensate.
Steam network in a process plant - Steam has been a popular mode of conveying energy since the industrial revolution. Steam is used for generating power, used in process industries such as sugar, paper, fertilizer, refineries, petrochemicals, chemical, food, synthetic fibre and textiles. If the steam is being used to generate electrical power, higher pressures and superheat temperatures are desirable since steam turbines are more efficient at the temperatures and pressures. If the steam is being used only for process heating duties, no superheat is required. Superheated steam is not desirable since it results in lower heat transfer coefficients.
Steam tracing for piping and instruments - Steam tracing is heat tracing performed by circulating steam around process pipes to heat them. In engineering, the requirement for heating of piping and instruments, using steam tracing is normally indicated on the Piping and Instrument Diagram (P&IDs) or on the line lists.