Proper pump installation is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient operation of a pumping system. A poorly installed pump can lead to costly repairs, downtime, and even safety hazards.
In this post, the planning process for pump installation and the steps involved in installing and commissioning a pump has been discussed. By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this post, you can ensure that your pump is installed correctly and operates efficiently.
Planning the installation
Proper planning is a critical step in ensuring a successful pump installation. Before starting the installation process, it's important to carefully consider the requirements of the pumping system and the site where the pump will be installed.
- Selecting the right location for the pump: The first step in planning a pump installation is to select the right location for the pump. Considerations such as accessibility, proximity to the source of the liquid, and ease of maintenance should be taken into account. It's also important to ensure that the pump is installed in a location that is safe and meets any relevant regulatory requirements.
- Ensuring the foundation is strong enough to support the pump: The foundation is a crucial component of a pump installation, as it provides the support necessary to keep the pump stable and prevent vibrations. Before installing the pump, it's important to ensure that the foundation is strong enough to support the weight of the pump and any associated equipment.
- Determining the best orientation for the pump: The orientation of the pump can have a significant impact on its performance and longevity. The best orientation for the pump will depend on factors such as the type of pump, the flow rate, and the direction of the incoming liquid. It's important to consult the manufacturer's guidelines to determine the optimal orientation for the specific pump being installed.
Installing the pump
Once the planning phase is complete, the actual installation process can begin. Installing a pump involves several key steps, which are discussed here.
1. Preparing the site: Before installing the pump, it's important to prepare the site properly. This may involve clearing any debris, leveling the ground, and ensuring that there is adequate space for the pump and any associated equipment.
2. Installing the foundation: The foundation provides the support necessary to keep the pump stable and prevent vibrations. To install the foundation, follow the manufacturer's guidelines and ensure that the concrete is poured to the correct depth and allowed to cure for the recommended amount of time.

Use of proper pump foundations and base plates can reduce the vibration and correspondingly increase the life of mechanical seals and bearings etc.
Check detailed post on Pump foundation and Pump base plates.
3. Connecting the piping and electrical wiring: Once the foundation is in place, the piping and electrical wiring can be connected. It's important to use the correct piping and fittings for the specific pump being installed and to ensure that all connections are tight and secure. The electrical wiring should also be installed according to the manufacturer's guidelines and any relevant electrical codes.
4. Testing the pump: After the piping and wiring are connected, the pump can be tested to ensure that it is functioning correctly. This may involve priming the pump, checking for leaks, and monitoring the pump's performance to ensure that it is meeting the required specifications.
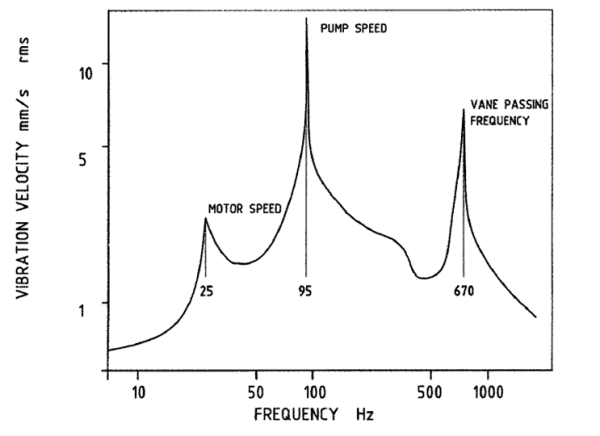
Study different methods used for testing of pumps, including performance testing, NPSH testing, endurance testing, hydrostatic testing, etc.
Pump Suction Piping
Proper installation of suction piping is crucial for optimal pump performance. In addition to the considerations mentioned in the previous section, the use of reducers in suction piping requires additional attention to avoid negative effects on pump performance.
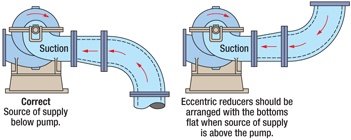
Check this post to study why we need a reducer in pump suction piping and expander at pump outlet?
Also check this detailed post on use of eccentric reducer in pump suction piping.
Pump Mechanical Seals
Pump mechanical seals are devices which keep or seal the pumped fluid in the pump casing, thus avoiding leakages and costly loss of pumped product. Since approximately 1950s, mechanical seals have almost totally eliminated inefficient and costly gland packings. They are installed at the place where the pump shaft enters or leaves the casing. There are various styles, configurations and sizes of mechanical seals. However, all of them employ the basic principle of stationary and rotating face combinations.
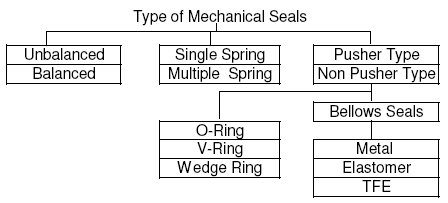
Explore what pump mechanical seals are, how they work and their different types such as - inside seals, outside seals, pusher seals, etc.