Rotary compressors are a type of positive displacement pumps that use a rotary motion to compress gas. They are used in wide range of industries such as HVAC, refrigeration and gas compression.
In this post we will explore about how rotary compressors work along with types of it.
Table of content
1. What is a Rotary Compressor?
2. Types of Rotary Compressors
2.1. Helical screw compressor
2.2. Sliding Vane Compressor
2.3. Scroll Compressor
2.4. Liquid Ring Compressor
2.5. Lobe Compressors
What is a Rotary Compressor?
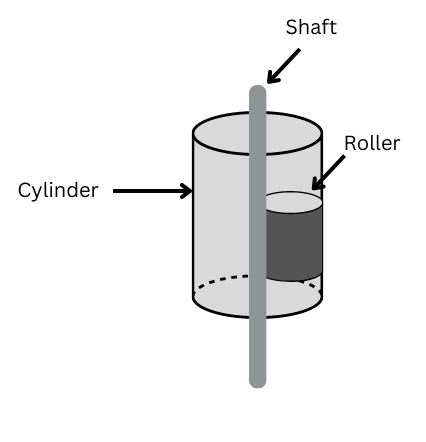
Rotary compressor produces compressed fluid by the rotary movement of rotating elements. Rotary compressors use rotating elements to compress a gas. These compressors work by trapping gas between rotating element and stationary element. This results in compression of gas by reducing the volume. The compressed gas is then discharged at a higher pressure.
Types of Rotary Compressors
There are five main types of rotary compressors. Each type has been thoroughly discussed in this post. Each type has its own unique design and operating principles.
Helical screw compressor
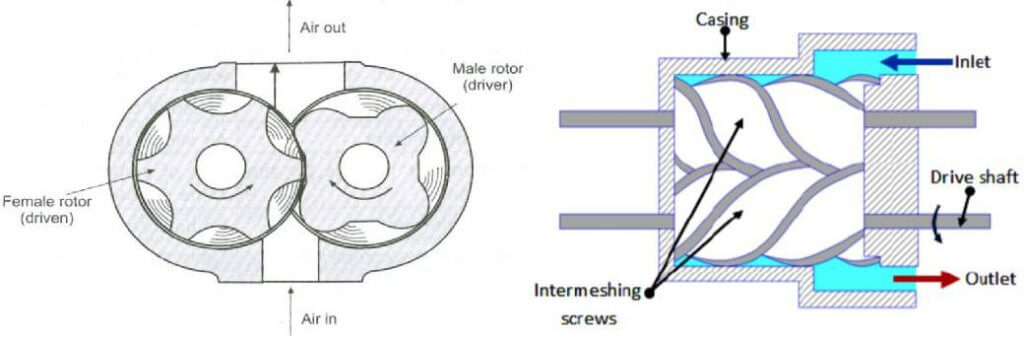
Screw compressors have two intermeshing rotors with helical lobes. The compressor draws in gas or air through an intake port. The gas is then trapped between the rotors and the housing. As the rotors rotate, the gas is trapped between the lobes and compressed as the volume between the rotors decreases. The compressed gas is then discharged through an outlet port. The compression process is continuous, resulting in a steady flow of compressed gas or air. The compressed gas is then discharged through a discharge port and sent to its intended application.
Screw compressors are known for their high efficiency, low noise levels, and minimal maintenance requirements. However, they are more expensive than other types of compressors, and they may not be suitable for certain types of gases or operating conditions.
Sliding Vane Compressor
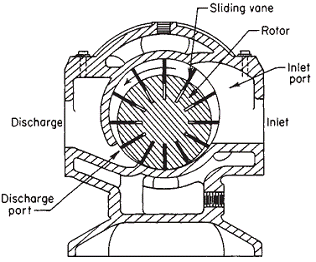
Vane compressors have a rotor with several slots that hold sliding vanes. The rotor and vanes rotate together, and as the rotor turns, the vanes slide in and out of their slots. This results in trapping and compression of gas. The compressed gas is then discharged through an outlet port. Vane compressors are known for their simplicity, low cost, and reliability. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure applications or for gases that contain abrasive particles.
Scroll Compressor

Scroll compressors have two interleaved spiral-shaped scrolls. As one scroll orbits around the other, the pockets between the scrolls decrease in volume, compressing the gas. The compressed gas is then discharged through an outlet port. Scroll compressors are known for their high efficiency, low noise levels, and minimal maintenance requirements. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure applications or for gases with high moisture content.
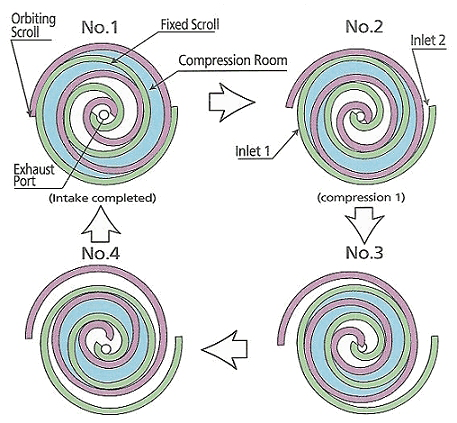
Check the given post to learn about how scroll compressors work along with structure, applications, advantages & disadvantages of it.
Liquid Ring Compressor
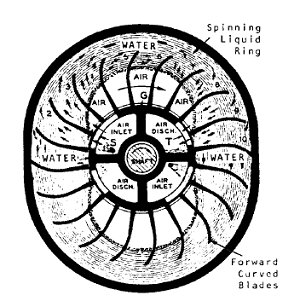
A liquid ring compressor is a type of rotary compressor that uses a liquid ring to compress gas or air. The compressor draws in gas or air through an intake port. The gas is then trapped between the rotor and the liquid ring. As the rotor rotates, the liquid ring creates a seal around the rotor, compressing the gas or air. The compression process is continuous, resulting in a steady flow of compressed gas or air. The compressed gas is then discharged through a discharge port and sent to its intended application.
The liquid ring in a liquid ring compressor is typically made of water or other liquids with low vapor pressures. The liquid ring creates a seal around the rotor and acts as a piston to compress the gas or air. As the rotor rotates, the liquid ring creates a centrifugal force that helps to maintain the seal and compress the gas or air.
Liquid ring compressors are known for their high reliability and durability. They have few moving parts and can operate continuously without the risk of overheating. They are also able to handle wet and dirty gases, making them ideal for applications that involve gases with high levels of moisture or contaminants.
Lobe Compressors
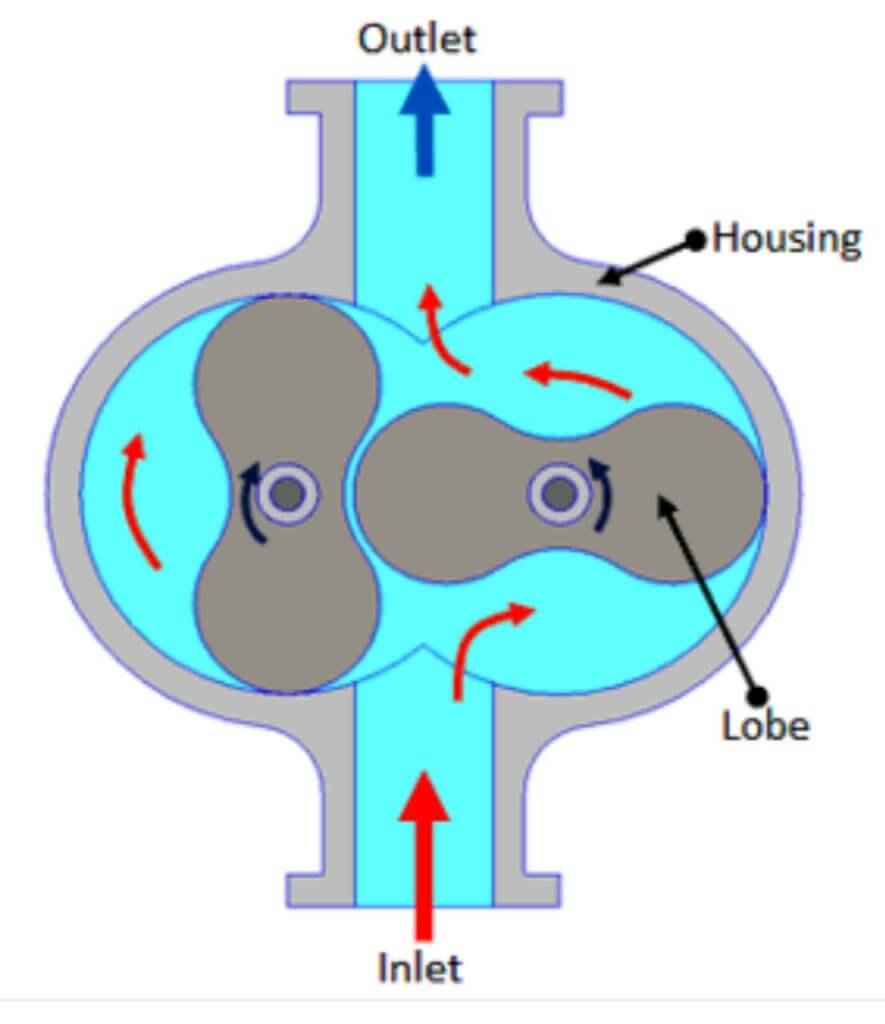
Lobe compressors uses two or more interlocking lobes to compress gas or air. The compressor draws in gas or air through an intake port. The gas is then trapped between the lobes and the housing. As the rotor rotates, the interlocking lobes compress the gas or air. The compression process is continuous, resulting in a steady flow of compressed gas or air. The compressed gas is then discharged through a discharge port and sent to its intended application.
The lobes in a lobe compressor are typically made of cast iron or steel and are designed to interlock with each other. As the rotor rotates, the lobes rotate in opposite directions, trapping and compressing the gas or air between them. Lobe compressors typically have two, three, or four lobes, depending on the required level of compression.
Lobe compressors They have few moving parts, making them easy to maintain and repair. They are also able to handle a wide range of gas compositions and are not affected by changes in gas viscosity or pressure. However, they are typically more expensive than some other types of compressors.
Overall, each type of rotary compressor has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The choice of which type to use depends on the specific application and operating conditions. For example, screw compressors may be preferred for applications that require high efficiency and low noise levels, while vane compressors may be preferred for applications that require simplicity and reliability at a low cost.