Important gasification reactions and stages
Gasification is a process of converting carbonaceous fuel into gaseous product with a usable heating value. Carbonaceous fuel includes solids, liquids and gases such as coals, biomass, residual oils and natural gas. Gasification is not a single step process and involves following subprocesses / stages and corresponding gasification reactions.
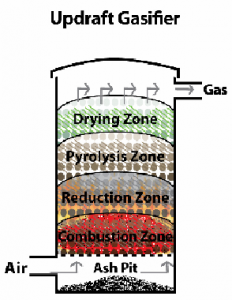
Drying of fuel
Generally all fuel feed contains moisture into it. At 100 degC water is evaporated. While drying, feed doesn’t experience any kind of decomposition.
Devolatilization
During devolatilization process three kind of products come out : Solids, liquids and gases. Ratio of the product is influenced by the chemical composition of feed. Heating value of the gas produced is 3.5-8.9MJ/m3. After devolatilization resulting feed is called char.
Oxidation of char
Oxygen present in air is partially consumed in the combustion of hydrocarbon gases while the rest is consumed in the heterogeneous reaction with char. Oxidation takes place in the temperature range of 700-1000 degC. C + O2 ↔ CO2 + 393.8 MJ/kgmol Hydrogen in feed reacts with oxygen to produce steam. H2 + O2 ↔ H2O + 239 MJ/kgmol
Reduction in absence of oxygen
In the reduction zone a number of reaction takes place in the absence of oxygen. Principal reaction that takes place inside the reactor are mentioned below.
Boudouard Reaction:
CO2 + C ↔ 2CO – 172.6 MJ/kgmol
Water-gas reaction:
C + H2O ↔ CO + H2 – 131.4 MJ/kgmol
Water shift reaction:
CO + H2O ↔ CO2 + H2 + 41.2 MJ/kgmol
Methane production reaction:
C + 2H2↔ CH4 + 75 MJ/kgmol Because most of the reactions are endothermic, temperature of gas goes down at this stage. if complete gasification takes place then no carbon is left only ash is left.
Schematic of a typical gasifier
Following figure represents different zones in a typical gasifier. The gasifier shown here is of upward draft type.