A falling film evaporator is a popular type of industrial evaporator used in many industries to concentrate or separate solutions. The name "falling film" comes from the way the liquid mixture flows down the walls of the tubes in a thin film under the influence of gravity. The purpose of this evaporator is to remove the solvent components from the liquid mixture, leaving behind a more concentrated solution.
Table of content:
Falling film evaporator design
How does a falling film evaporator work?
Falling film evaporator applications
Advantages of falling film evaporator
Disadvantages of falling film evaporator
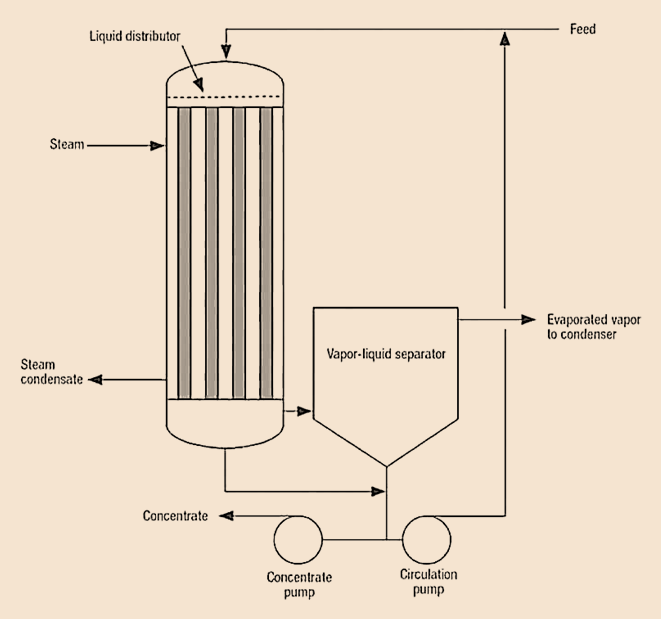
Falling film evaporator design
A falling film evaporators are designed as a shell-and-tube heat exchanger where a liquid mixture enters at the top of the tubes and flows down the walls of the tubes in the form of a thin film under the influence of gravity.
The basic components of a falling film evaporator are:
- Heat Exchanger: A shell-and-tube heat exchanger that has a series of vertical tubes through which the liquid mixture flows down. The heat exchanger has a steam or hot water jacket surrounding the tubes, which heats the tubes to a temperature higher than the boiling point of the mixture.
- Distributor: A distributor at the top of the tubes that ensures a uniform distribution of the liquid mixture.
- Vapor Separator: A vapor separator at the top of the evaporator that separates the vapor from the liquid and sends it to a condenser.
- Condenser: A condenser that cools and condenses the vapor back into a liquid state.
- Product Tank: A product tank that collects the concentrated liquid from the bottom of the evaporator.
How does a falling film evaporator work?
During the operation of falling film evaporator, the liquid mixture enters the tubes from the distributor and flows down as a thin film.
As the mixture flows down the tubes, it is heated by the steam or hot water jacket, and the solvent component evaporates, leaving behind a more concentrated liquid.
The vapor generated rises up through the central portion of the tubes and exits at the top of the evaporator. The concentration of the liquid increases as it flows down the tubes, and the concentrated liquid exits at the bottom of the evaporator and is collected in the product tank.
Falling film evaporator applications
Falling film evaporators are used in a wide range of industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, chemical processing, and petrochemicals. Here are some examples of products and applications that use falling film evaporators:
- Falling film evaporators are used to concentrate milk and dairy products such as cream, whey, and lactose. The high heat transfer rate and short residence time of falling film evaporators make them ideal for processing heat-sensitive dairy products.
- Falling film evaporators are used to concentrate acids, alkalis, and solvents in the chemical processing industry. The low holdup volume of falling film evaporators reduces the risk of product degradation, making them a popular choice for handling corrosive and reactive chemicals.
- Falling film evaporators are used to purify and concentrate pharmaceutical intermediates and active ingredients. The low residence time and uniform heating of falling film evaporators help to preserve the quality of heat-sensitive pharmaceutical products.
- Falling film evaporators are used to purify and concentrate crude oil, refining streams, and other petrochemicals. The high heat transfer rate of falling film evaporators makes them ideal for handling high-viscosity fluids and heavy fractions.
Advantages of falling film evaporator
Here are some of the advantages of falling film evaporators:
- High Efficiency: Falling film evaporators have a high heat transfer coefficient due to the continuous renewal of the evaporating surface, which leads to a higher evaporation rate and lower operating costs.
- Low Holdup Volume: Falling film evaporators have a low holdup volume, which reduces the risk of product degradation and improves the quality of the final product.
- Short Residence Time: Falling film evaporators have a short residence time, which is ideal for processing heat-sensitive products and reduces the risk of thermal degradation.
- Low Maintenance: Falling film evaporators require less maintenance than other types of evaporators, which reduces downtime and operating costs.
- Energy Efficient: Falling film evaporators require less energy than other types of evaporators, which makes them a cost-effective solution for many applications.
Disadvantages of falling film evaporator
There are some potential disadvantages to consider while selecting falling film evaporator. Here are some of the disadvantages of falling film evaporators:
- Product Foaming: Falling film evaporators can be prone to product foaming, which can reduce the efficiency of the evaporation process and increase the risk of product contamination.
- Higher Capital Costs: Falling film evaporators can have higher capital costs than some other types of evaporators due to their complex design and construction.
- Limited Viscosity Range: Falling film evaporators are best suited for processing liquids with low to medium viscosities. High-viscosity liquids may require special modifications to the design, which can increase costs and reduce efficiency.
- Limited Solids Handling: Falling film evaporators are not well-suited for processing liquids with high levels of solids or impurities, which can clog the evaporator and reduce efficiency.
- Limited Capacity: Falling film evaporators may have limited capacity compared to some other types of evaporators, which can limit their usefulness for larger-scale processing operations.