Evaporation is a widely used process in various industries for the concentration of liquids. The rising film evaporator is a type of heat exchanger that is commonly used for this purpose. It is a highly efficient and effective way of evaporating large volumes of liquid in a short amount of time. In this post, we will discuss in detail the working principle, design, advantages and disadvantages of a rising film evaporator.
Table of content:
What is a rising film evaporator?
Working principle of rising film evaporator
Rising film evaporator design
Advantages of rising film evaporator
Disadvantages of rising film evaporator
What is a rising film evaporator?
A rising film evaporator is a type of vertical shell-and-tube heat exchanger that is commonly used in industries such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceuticals. Its main purpose is to concentrate a liquid by evaporating the solvent or water from it.
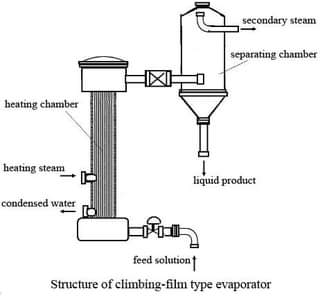
A rising film evaporator is a type of evaporator commonly used in the process industry for the concentration of solutions. It is a forced circulation evaporator where a liquid is pumped through a vertical tube or a bundle of tubes, forming a thin film along the walls of the tube. The term "rising film" refers to the thin layer of liquid that rises against gravity through a heated tube or vessel, where it is evaporated due to the heat applied. This process helps to separate the liquid from any solid components or impurities, leaving behind a more concentrated liquid or solid product.
Rising film evaporators are highly efficient and effective in evaporating large volumes of liquid in a short amount of time. They have several advantages over other types of evaporators, including low fouling, low residence time, and low energy consumption. They are also suitable for handling heat-sensitive and viscous liquids. However, they require careful control to prevent dry out and ensure uniform flow distribution.
Working principle of rising film evaporator
A rising film evaporator is a vertical cylindrical vessel that consists of a set of tubes through which the liquid to be concentrated flows. The liquid is heated by a heating medium, such as steam or hot oil, which is circulated around the tubes. As the liquid is heated, it starts to boil and form vapor bubbles. The vapor rises through the tubes, causing the liquid to form a thin film on the inside of the tubes. The film of liquid is heated and evaporated as it rises, and eventually, the concentrated liquid is collected at the top of the evaporator.
The design of a rising film evaporator is such that the liquid flow is maintained in a thin film on the inside of the tubes. This is achieved by ensuring that the velocity of the liquid is higher than the velocity of the vapor. The film of liquid is heated by the heating medium and evaporated as it rises through the tubes. The vapor is then collected at the top of the evaporator and condensed back into liquid form for further use.
Rising film evaporator design
The design of a rising film evaporator is critical to its efficient operation. The following are the key design parameters:
- Tube diameter and length - The diameter and length of the tubes are critical to ensure that the liquid flows in a thin film on the inside of the tubes. The diameter of the tubes is typically between 25 mm and 75 mm, while the length is between 4 m and 8 m.
- Liquid feed rate - The liquid feed rate is critical to ensure that the liquid film is maintained on the inside of the tubes. The liquid feed rate should be such that the liquid velocity is higher than the vapor velocity.
- Heating medium temperature and flow rate - The heating medium temperature and flow rate are critical to ensure that the liquid is heated and evaporated efficiently. The temperature of the heating medium should be high enough to ensure efficient evaporation, while the flow rate should be high enough to ensure that the heating medium is evenly distributed around the tubes.
- Vapor outlet design - The design of the vapor outlet is critical to ensure that the vapor is collected efficiently. The vapor outlet should be located at the top of the evaporator and designed to prevent any liquid carryover.
Advantages of rising film evaporator
Rising film evaporators have several advantages over other types of evaporators.
- High efficiency - Rising film evaporators are highly efficient in evaporating large volumes of liquid in a short amount of time. This is due to the fact that the heat transfer coefficient is high due to the thin liquid film on the inside of the tubes, which provides a large surface area for heat transfer.
- Low residence time - The residence time of the liquid in the evaporator is low, which minimizes the chances of degradation or thermal damage to the product being processed.
- Low fouling - Rising film evaporators are less prone to fouling compared to other types of evaporators because the liquid film flows over the surface of the tubes, which prevents the buildup of deposits.
- Low energy consumption - Rising film evaporators require less energy to operate compared to other types of evaporators, as the liquid film on the inside of the tubes provides a large surface area for heat transfer, which reduces the overall energy required for evaporation.
- Suitable for heat-sensitive products - Rising film evaporators are suitable for processing heat-sensitive products, as the low residence time and gentle heating minimize the chances of thermal damage or product degradation.
- High capacity - Rising film evaporators can process large volumes of liquid in a short amount of time, making them ideal for industrial-scale processing.
Disadvantages of rising film evaporator
While rising film evaporators have many advantages, they also have a few disadvantages that should be considered.
- High initial cost - Rising film evaporators have a high initial cost compared to other types of evaporators, which may make them less attractive for some applications.
- Sensitive to liquid flow rates - Rising film evaporators require precise control of the liquid flow rate to maintain the thin film on the inside of the tubes. If the liquid flow rate is too low, the liquid film may not form, while if the flow rate is too high, the liquid film may become unstable.
- Limited scalability - The size of a rising film evaporator is limited by the need to maintain a thin film on the inside of the tubes. This may make it difficult to scale up the process for large-scale production.
- Limited versatility - Rising film evaporators are best suited for processing low-viscosity liquids. They may not be suitable for processing high-viscosity liquids or liquids with high solids content.
- Requires regular cleaning - Although rising film evaporators are less prone to fouling than other types of evaporators, they still require regular cleaning to prevent the buildup of deposits on the tube surfaces.