Scraped surface heat exchanger is a component in industries, allowing for efficient heating and cooling of high-viscosity products. These exchangers are designed to handle fluids that tend to foul or build up on the heat transfer surface, providing improved heat transfer efficiency and reduced maintenance costs.
In this post, we will explore, the operation and advantages of scraped surface heat exchangers, as well as their applications process industry.
Table of content:
1. What is scraped surface heat exchanger?
2. How do scraped surface heat exchangers work?
3. Applications of scraped surface heat exchangers
4. Advantages of scraped surface heat exchangers
What is scraped surface heat exchanger?
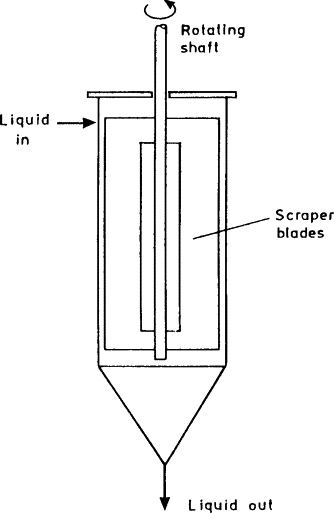
A scraped surface heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger that is designed to handle viscous or sticky fluids that tend to foul or build up on the heat transfer surface. The scraped surface heat exchanger consists of a cylindrical shell containing a series of closely spaced, rotating, and scraping blades.
The blades scrape the fluid off the heat transfer surface, preventing fouling and ensuring efficient heat transfer. The heat transfer surface can be jacketed or unjacketed, depending on the application.
How do scraped surface heat exchangers work?
As the fluid flows through the scraped surface heat exchanger, the blades scrape the fluid off the heat transfer surface, preventing fouling and ensuring efficient heat transfer. The scraped material is then forced to flow through the gaps between the blades, creating a turbulent flow that further enhances heat transfer.
The scraping action of the blades provides several benefits over traditional heat exchangers. For one, it reduces fouling and buildup on the heat transfer surface, allowing for a longer operating time between cleanings.
Additionally, the turbulent flow created by the blades enhances heat transfer by breaking up any boundary layers that may form on the surface of the heat transfer fluid. This results in higher heat transfer coefficients and improved overall efficiency.
Applications of scraped surface heat exchangers
Scraped surface heat exchangers are commonly used in the food industry for processing high-viscosity products that would be difficult to handle with traditional heat exchangers. Some examples of these products include chocolate, peanut butter, cheese, and other dairy products.
In addition to improving heat transfer efficiency and reducing fouling, the use of scraped surface heat exchangers can also improve product quality and consistency. By providing precise temperature control and minimizing thermal stress on the product, scraped surface heat exchangers can help ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications and is of high quality.
Scraped surface heat exchangers can also be used in other industries, such as chemical processing and pharmaceuticals, where high-viscosity fluids are common. In the chemical industry, scraped surface heat exchangers can be used for the processing of resins, polymers, and adhesives, while in the pharmaceutical industry, they can be used for the processing of creams, ointments, and gels.
Advantages of scraped surface heat exchangers
Scraped surface heat exchangers offer several advantages over traditional heat exchangers, making them an ideal choice for processing high-viscosity food products.
1. Improved Heat Transfer Efficiency: By maintaining a clean heat transfer surface, scraped surface heat exchangers provide improved heat transfer efficiency compared to traditional heat exchangers. This means that more heat can be transferred in a shorter amount of time, leading to faster processing times and increased throughput.
2. Reduced Fouling: Because the blades of scraped surface heat exchangers scrape the product off the heat transfer surface, there is less fouling and buildup over time. This not only reduces maintenance costs, but also improves the consistency and quality of the final product.
3. Compared to other types of heat exchangers, such as plate heat exchangers or shell and tube heat exchangers, scraped surface heat exchangers offer several advantages.
For example, plate heat exchangers are prone to fouling and may not be suitable for high-viscosity products, while shell and tube heat exchangers may require frequent cleaning and have lower heat transfer efficiency.
Scraped surface heat exchangers are more efficient and can handle higher viscosities. They are also less prone to fouling and require less frequent cleaning, which can result in significant cost savings over time.