Evaporators and condensers are two types of heat exchangers that play critical roles in a wide range of industries. An evaporator is a device that removes heat from a liquid by converting it to vapor, while a condenser is a device that removes heat from a vapor by converting it to a liquid. Evaporators and condensers are essential components in many industrial processes, enabling the efficient transfer of heat and the production of a wide range of products.
Table of content:
Evaporator
Condenser
Differences between evaporators and condensers
Evaporator
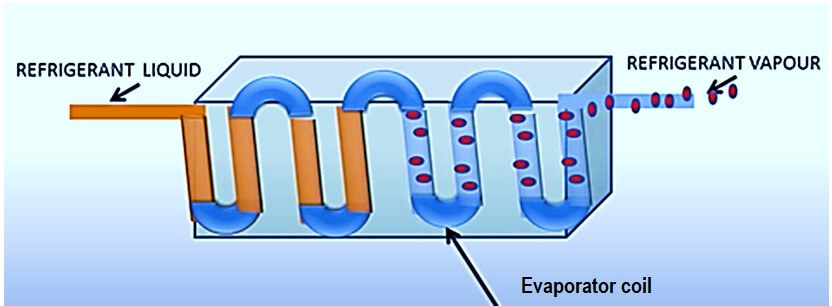
The evaporator is a critical component in a refrigeration system that facilitates the transfer of heat from the surrounding environment to the refrigerant liquid, causing it to evaporate and turn into a low-pressure, low-temperature vapor.
The evaporator is a heat exchanger that is typically located within a chamber or enclosure. Refrigerant liquid, typically in the form of a low-pressure, low-temperature liquid, enters the evaporator and circulates through a series of coils or tubes. As it passes through the evaporator, the refrigerant liquid absorbs heat from the surrounding environment, causing it to evaporate and turn into a low-pressure, low-temperature vapor.
To facilitate the transfer of heat from the chamber to the refrigerant liquid, the evaporator coils are placed within the chamber and are in contact with the material being cooled. The inlet and outlet pipes for the refrigerant liquid are connected to the evaporator coil, with the inlet pipe providing a path for the liquid to enter the coil and the outlet pipe providing a path for the vaporized refrigerant to exit the coil.
As the refrigerant liquid circulates through the evaporator coil, it absorbs latent heat from the surrounding environment, which causes it to undergo a phase change and convert into a low-pressure, low-temperature vapor.
There are several types of evaporators, each with its own unique design and operating characteristics. One type of evaporator is the natural circulation evaporator, which relies on gravity to circulate the liquid through the evaporator. Another type is the forced circulation evaporator, which uses a pump to circulate the liquid through the evaporator. A third type is the falling film evaporator, which features a thin film of liquid that flows down the surface of the heat transfer tubes or plates, allowing for efficient heat transfer.
Condenser
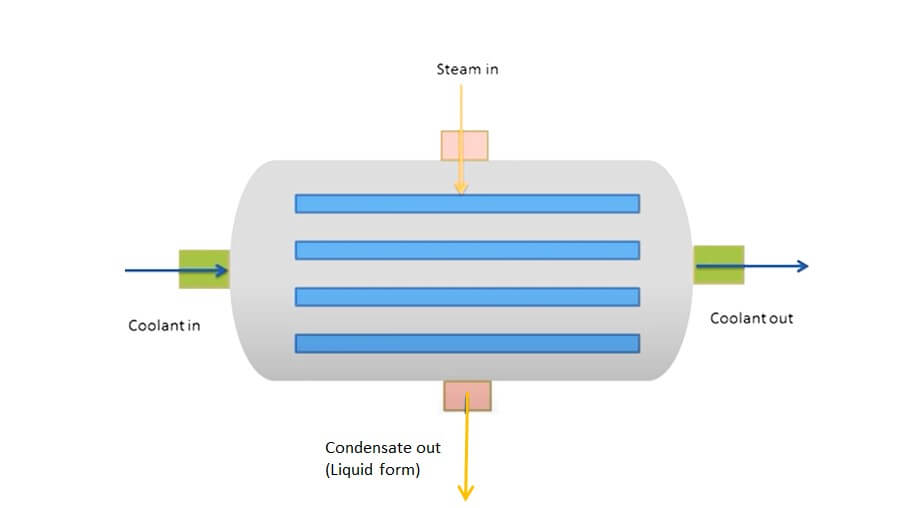
In both thermal power plants and refrigeration systems, the condenser is an essential component that plays a crucial role in the process of converting a fluid into a liquid form by removing its latent heat. The condenser typically uses water as a cooling medium.
The condenser chamber consists of water tubes through which cold water flows, while the hot fluid (usually steam) flows through valves into the chamber. As the steam flows through the chamber and comes into contact with the water flowing through the tubes, it releases its latent heat and is converted into a liquid.
The process of converting steam into a liquid form releases a large amount of heat, which must be dissipated into the environment in order to maintain the proper operating temperature. This is typically accomplished by circulating cooling water through the condenser, which absorbs the heat and carries it away from the system.
There are several types of condensers, each with its own unique design and operating characteristics. One type is the water-cooled condenser, which uses water as the cooling medium and is typically more efficient than air-cooled condensers. Another type is the air-cooled condenser, which uses air as the cooling medium and is often used in applications where water is scarce or expensive. A third type is the evaporative condenser, which removes heat from a process or system by using the evaporation of water.
Differences between evaporators and condensers
Evaporators and condensers are two types of heat exchangers that are commonly used in industrial processes. While both are used to transfer heat between two fluids, they function in opposite ways and have different applications.
1. Evaporators are used to remove heat from a liquid or solution, causing it to evaporate and become a vapor. This process is used in applications such as refrigeration, food processing, and wastewater treatment, where the removal of water or other liquids is necessary.
Condensers, on the other hand, are used to remove heat from a vapor or gas, causing it to condense into a liquid. This process is used in applications such as power generation, chemical manufacturing, and refrigeration, where the conversion of a vapor or gas to a liquid is necessary.
2. Evaporators work by circulating a hot fluid, such as steam or hot water, over a series of tubes or plates that contain the liquid to be evaporated. As the hot fluid comes into contact with the liquid, it transfers its heat to the liquid, causing it to evaporate.
Condensers work by circulating a cold fluid, such as water or air, over a series of tubes or plates that contain the vapor or gas to be condensed. As the cold fluid comes into contact with the vapor or gas, it absorbs its heat, causing it to condense into a liquid.
3. Evaporators primarily use convection heat transfer, where heat is transferred through the motion of the fluid. Condensers primarily use conduction heat transfer, where heat is transferred through direct contact between the fluids.
4. In many industrial processes, evaporators and condensers are used together in a series of heat exchangers to achieve specific goals. For example, in a power generation plant, steam is used to drive a turbine and generate electricity. After passing through the turbine, the steam is sent to a condenser, where it is converted back into water for reuse in the power generation process.
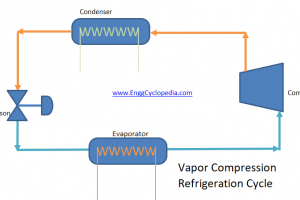
In a refrigeration system, an evaporator is used to remove heat from the refrigerant, causing it to evaporate and cool the surrounding environment. The refrigerant is then sent to a condenser, where it is converted back into a liquid and the heat is released into the environment.