A water-cooled condenser is a type of heat exchanger used in process industries to remove heat from a hot process fluid or gas by transferring it to a cooling water stream. Water-cooled condensers are commonly used in industries such as power generation, petrochemicals, and refrigeration to maintain consistent process fluid temperatures and improve product quality and process efficiency.
Table of content:
What is a water cooled condenser?
How does water cooled condenser works?
Water cooled condenser diagram
Advantages and disadvantages of water cooled condenser
What is a water cooled condenser?
A water-cooled condensers are a type of heat exchanger that is used in industrial applications to remove heat from a hot fluid or gas by transferring it to a cooling water stream. The basic principle behind a water-cooled condensers is that the process fluid is passed through a series of tubes while cooling water is circulated around the tubes in a separate chamber.
Heat is transferred from the process fluid to the cooling water, which is then discharged at a higher temperature. This helps to maintain consistent process fluid temperatures, improve product quality and process efficiency, and reduce environmental impact.
How does water cooled condenser works?
A water-cooled condenser works by transferring heat from a hot process fluid or gas to a cooling water stream. The basic design of a water-cooled condenser consists of a set of tubes through which the process fluid flows, and a separate chamber that contains cooling water. The process fluid flows through the tubes, while the cooling water is circulated around the tubes in the separate chamber.
As the hot process fluid flows through the tubes, heat is transferred from the process fluid to the cooling water that surrounds the tubes. This causes the process fluid to lose heat and cool down, while the cooling water absorbs the heat and becomes hotter. The cooling water is then discharged at a higher temperature and the cooled process fluid continues on through the process.
The efficiency of the heat transfer process in a water-cooled condenser depends on several factors, including the flow rate of the process fluid and cooling water, the temperature difference between the process fluid and cooling water, and the surface area and material of the tubes.
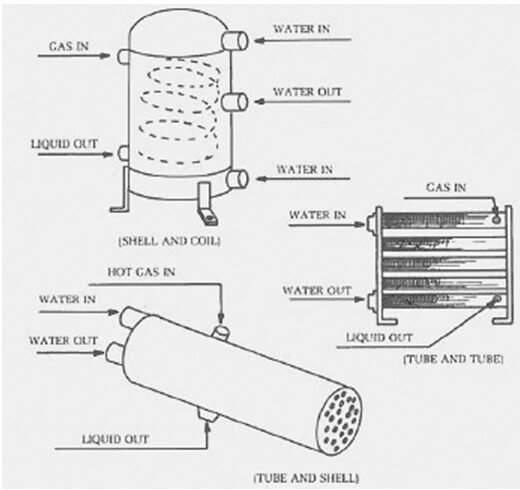
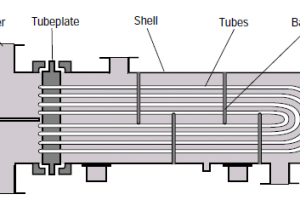
Water cooled condenser diagram
The above schematic shows three different types of water cooled condensers.
Advantages and disadvantages of water cooled condenser
Advantages
There are several advantages to using water-cooled condensers:
- Water-cooled condensers are generally more efficient than air-cooled condensers because water has a higher heat capacity and thermal conductivity than air. This means that water can absorb more heat and transfer it more quickly than air.
- Because water-cooled condensers are not affected by changes in ambient temperature or humidity, they can provide consistent cooling performance regardless of external conditions.
- Water-cooled condensers can be more compact than air-cooled condensers because they don't require large fans or air flow ducts. This can be especially important in situations where space is limited.
- Water-cooled condensers are generally quieter than air-cooled condensers because they don't require large fans to move air over the cooling fins.
- Water-cooled condensers can consume less energy than air-cooled condensers because they don't require large fans to move air over the cooling fins. Additionally, water-cooled systems can be optimized for higher efficiency through the use of variable speed pumps and other control strategies.
Disadvantages
There are several disadvantages to using water-cooled condensers:
- Water-cooled condensers require a reliable source of cooling water, which may not be available in all locations or may be subject to restrictions during times of drought or other water shortages.
- The quality of the cooling water can affect the performance and lifespan of the condenser. Water that is too hard, too acidic, or contains high levels of minerals or contaminants can cause scaling, corrosion, or other problems.
- Water-cooled condensers require regular maintenance to prevent scaling, corrosion, and other issues related to water quality. This can include regular cleaning and treatment of the cooling water, as well as inspection and repair of the condenser itself.
- Water-cooled condensers can be more expensive to install and operate than air-cooled condensers, due to the additional costs associated with pumping and treating the cooling water.
- The use of large amounts of water for cooling can have an environmental impact, particularly in areas with limited water resources.