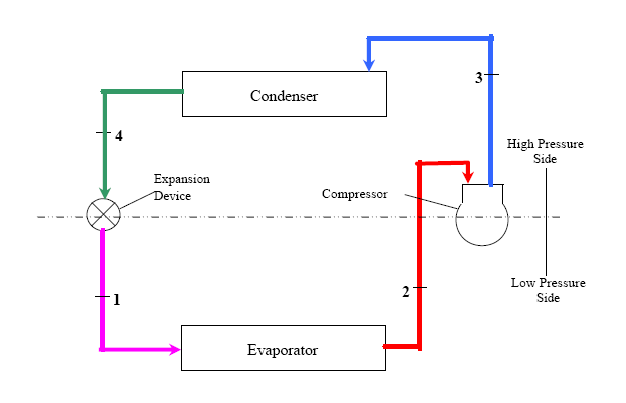
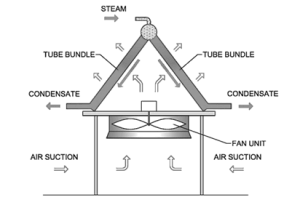
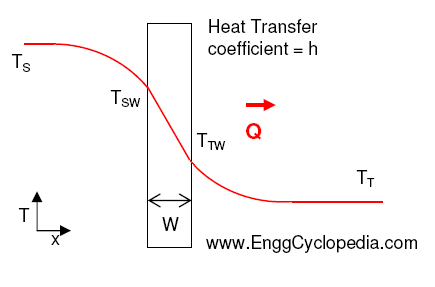
Heat exchangers are essential components in many industries, including chemical, power generation, HVAC, and refrigeration. They play a crucial role in transferring heat from one fluid to another while keeping them separated. Learn everything about heat exchangers including their types, working principle, design & calculations, design software and P&ID symbols in this post.
How do heat exchangers work?
Selection of a particular type of heat exchanger depends on - the nature of the two fluid streams, their pressure, temperature, flow rates and required heat transfer rate. Therefore it is important to understand, how do heat exchangers work in order to make an informed decision about which heat exchanger can be used in a given situation.
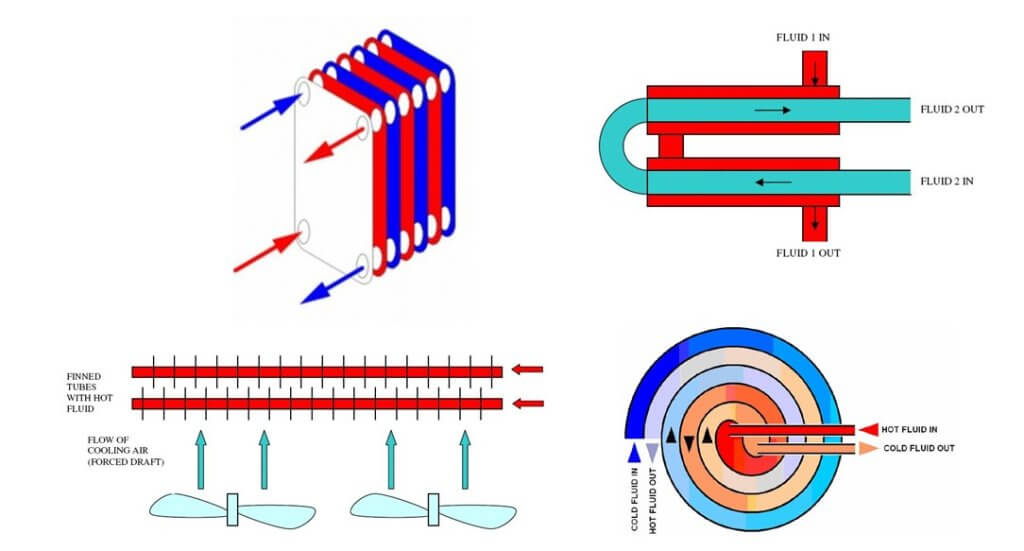
Heat Exchanger Types
Heat transfer equipment can be classified into various types based on structure, phases of fluid involved, and the principle of operation.
1. Plate and Frame Heat Exchanger
2. Spiral Heat Exchanger
3. Plate-Fin Heat Exchanger
4. Air coolers
5. Double Pipe Heat Exchanger
6. Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
7. Kettle Type Heat Exchanger
8. Condenser
9. Evaporator
10. Regenerative Heat Exchanger
11. Twisted Tube Heat Exchanger
12. Scraped Surface Heat Exchanger
13. Coil Heat Exchangers
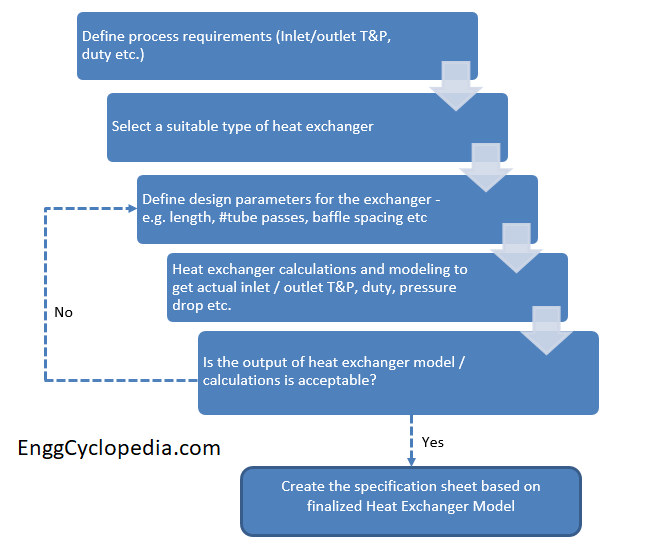
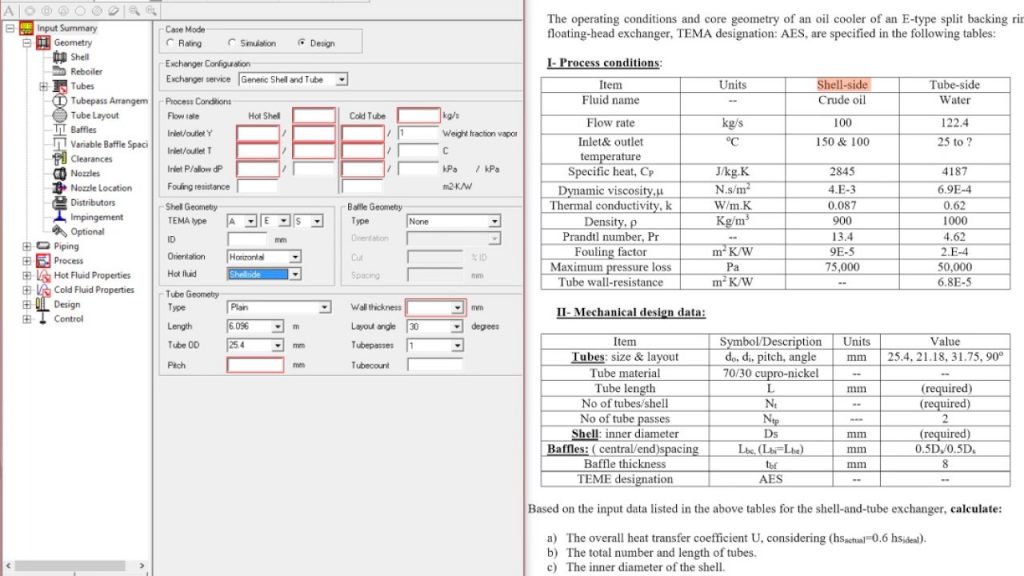
Heat Exchanger Design & Calculations
Properly sizing a heat exchanger is crucial to ensure that it can effectively transfer heat and meet the needs of the system it is being used in. Check this post to take a look at details that go into heat exchanger calculations and how to properly size a heat exchanger for your specific system. Following topics has been discussed in this post.
1. Heat exchanger design
2. Energy balance calculation
3. Calculation of heat transfer coefficient
4. Log mean temperature difference calculation
5. Heat exchanger area
6. Heat exchanger efficiency
7. Heat exchanger fouling factor
8. Heat exchanger approach temperature
9. Shell and tube heat exchanger design procedure
10. Shell and tube heat exchanger equations
11. Shell and tube heat exchanger pressure drop
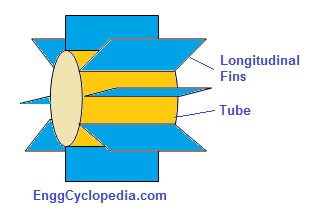
Finned tube heat exchangers
Finned tube exchangers are known for maximizing heat transfer surface area, by design. Finned tubes or tubes with extended outer surface area enhance the heat transfer rate by increasing the effective heat transfer area between the tubes and surrounding fluid. The fluid surrounding finned tubes maybe process fluid or air.
Finned tube heat exchangers are preferred when you have a low heat transfer coefficient on the outside of the tubes. In such cases the extra heat transfer area created by the fins helps in ensuring that required rate of heat transfer is made possible.
Heat exchanger fouling
Heat exchanger fouling is a commonly occurring problem in different kinds of heat exchangers. It results in changing the heat transfer surface and reducing the overall heat transfer rate through that surface.
Let's then look at why fouling occurs in a heat exchanger to begin with. There are a few different reasons. They make up for different types of fouling.

Heat exchanger design software
Most process engineers commonly rely on process simulation software to quickly perform heat exchanger design calculations. This post shows some commonly used heat exchanger design software tools which can help you.
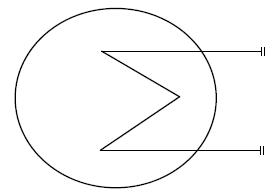
Heat exchanger P&ID symbols
P&ID diagrams, also known as Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams, are used to map out the design of engineering systems in various industries. These diagrams are essential for problem identification and troubleshooting, as they provide a clear representation of the system's components and their interconnections. It is important to know heat exchanger P&ID symbols to read P&ID diagrams.
This post shows commonly used P&ID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram) symbols for heat transfer equipment.